Ghrelin treatment reverses the reduction in weight gain and body fat in gastrectomised mice
- PMID: 15849166
- PMCID: PMC1774616
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2004.058578
Ghrelin treatment reverses the reduction in weight gain and body fat in gastrectomised mice
Abstract
Background and aims: The gastric hormone ghrelin has been reported to stimulate food intake, increase weight gain, and cause obesity but its precise physiological role remains unclear. We investigated the long term effects of gastrectomy evoked ghrelin deficiency and of daily ghrelin injections on daily food intake, body weight, fat mass, lean body mass, and bone mass in mice.
Methods: Ghrelin was given by subcutaneous injections (12 nmol/mouse once daily) for eight weeks to young female mice subjected to gastrectomy or sham operation one week previously.
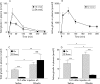
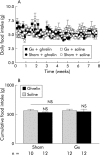
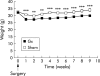
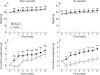
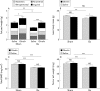
Results: Gastrectomy reduced plasma concentrations of total ghrelin (octanoylated and des-octanoylated) and active (octanoylated) ghrelin by approximately 80%. Immediately after injection of ghrelin, the plasma concentration was supraphysiological and was still elevated 16 hours later. Daily food intake was not affected by either gastrectomy or ghrelin treatment. The effect of ghrelin on meal initiation was not studied. At the end point of the study, mean body weight was 15% lower in gastrectomised mice than in sham operated mice (p<0.001); daily ghrelin injections for eight weeks partially prevented this weight loss. In sham operated mice, ghrelin had no effect on body weight. The weight of fat was reduced in gastrectomised mice (-30%; p<0.01). This effect was reversed by ghrelin, enhancing the weight of fat in sham operated mice also (+20%; p<0.05). Gastrectomy reduced lean body mass (-10%; p<0.01) and bone mass (-20%; p<0.001) compared with sham operated mice. Ghrelin replacement prevented the gastrectomy induced decrease in lean body mass but did not affect bone. In sham operated mice, ghrelin affected neither of these two parameters.
Conclusions: Ghrelin replacement partially reversed the gastrectomy induced reduction in body weight, lean body mass, and body fat but not in bone mass. In sham operated mice, ghrelin only increased fat mass. Our results suggest that ghrelin is mainly concerned with the control of fat metabolism and that ghrelin replacement therapy may alleviate the weight loss associated with gastrectomy.
Figures
References
-
- Date Y, Kojima M, Hosoda H, et al. Ghrelin, a novel growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide, is synthesized in a distinct endocrine cell type in the gastrointestinal tracts of rats and humans. Endocrinology 2000;141:4255–61. - PubMed
-
- Dornonville de la Cour C, Björkqvist M, Sandvik AK, et al. A-like cells in the rat stomach contain ghrelin and do not operate under gastrin control. Regul Pept 2001;99:141–50. - PubMed
-
- Rindi G, Necchi V, Savio A, et al. Characterisation of gastric ghrelin cells in man and other mammals: studies in adult and fetal tissues. Histochem Cell Biol 2002;117:511–19. - PubMed
-
- Hosoda H, Kojima M, Matsuo H, et al. Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin: two major forms of rat ghrelin peptide in gastrointestinal tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000;279:909–13. - PubMed
-
- Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, et al. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999;402:656–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
