Electrochemical and PM-IRRAS studies of the effect of cholesterol on the structure of a DMPC bilayer supported at an Au (111) electrode surface, part 1: properties of the acyl chains
- PMID: 15849259
- PMCID: PMC1366559
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.104.058347
Electrochemical and PM-IRRAS studies of the effect of cholesterol on the structure of a DMPC bilayer supported at an Au (111) electrode surface, part 1: properties of the acyl chains
Abstract
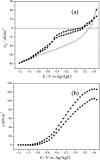
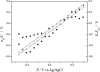
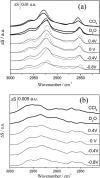
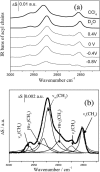
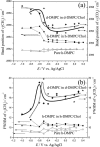
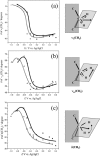
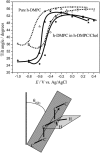
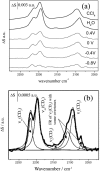
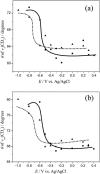
Charge density measurements and polarization modulation infrared reflection absorption spectroscopy were employed to investigate the spreading of small unilamellar vesicles of a dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine (DMPC)/cholesterol (7:3 molar ratio) mixture onto an Au (111) electrode surface. The electrochemical experiments demonstrated that vesicles fuse and spread onto the Au (111) electrode surface, forming a bilayer, at rational potentials -0.4 V < (E - Epzc) < 0.4 V or field strength <6 x 10(7) V m(-1). Polarization modulation infrared reflection absorption spectroscopy experiments provided information concerning the conformation and orientation of the acyl chains of DMPC molecules. Deuterated DMPC was used to subtract the contribution of C-H stretching bands of cholesterol and of the polar head region of DMPC from spectra in the C-H stretching region. The absorption spectra of the C-H stretch bands in the acyl chains were determined in this way. The properties of the DMPC/cholesterol bilayer have been compared with the properties of a pure DMPC bilayer. The presence of 30% cholesterol gives a thicker and more fluid bilayer characterized by a lower capacity and lower tilt angle of the acyl chains.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Electrochemical and PM-IRRAS studies of the effect of the static electric field on the structure of the DMPC bilayer supported at a Au(111) electrode surface.Langmuir. 2005 Jan 4;21(1):330-47. doi: 10.1021/la048710w. Langmuir. 2005. PMID: 15620322
-
Electrochemical and PM-IRRAS studies of the effect of cholesterol on the properties of the headgroup region of a DMPC bilayer supported at a Au(111) electrode.J Phys Chem B. 2006 Dec 28;110(51):26430-41. doi: 10.1021/jp0660132. J Phys Chem B. 2006. PMID: 17181303
-
Spectroelectrochemical studies of bilayers of phospholipids in gel and liquid state on Au(111) electrode surface.Bioelectrochemistry. 2004 Jun;63(1-2):137-47. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2003.12.004. Bioelectrochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15110264
-
Building biomimetic membrane at a gold electrode surface.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2010 Nov 14;12(42):13874-87. doi: 10.1039/c0cp00658k. Epub 2010 Sep 20. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2010. PMID: 20852809 Review.
-
Experimental and theoretical studies of emodin interacting with a lipid bilayer of DMPC.Biophys Rev. 2017 Oct;9(5):729-745. doi: 10.1007/s12551-017-0323-1. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Biophys Rev. 2017. PMID: 28940105 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A quantitative determination of lipid bilayer deposition efficiency using AFM.RSC Adv. 2021 Jun 2;11(32):19768-19778. doi: 10.1039/d1ra01920a. eCollection 2021 May 27. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35479201 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysical effects of electric fields on membrane water interfaces: a mini review.Eur Biophys J. 2007 Nov;36(8):967-72. doi: 10.1007/s00249-007-0168-9. Epub 2007 May 11. Eur Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17492435 Review.
-
Characterization of the interactions between fluoroquinolone antibiotics and lipids: a multitechnique approach.Biophys J. 2008 Apr 15;94(8):3035-46. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.114843. Epub 2008 Jan 4. Biophys J. 2008. PMID: 18178657 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular absorption of small molecules: free energy landscapes of melatonin binding at phospholipid membranes.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 8;10(1):9235. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65753-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32513935 Free PMC article.
-
Tethered bilayer lipid membranes studied by simultaneous attenuated total reflectance infrared spectroscopy and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy.J Phys Chem B. 2007 Apr 5;111(13):3515-24. doi: 10.1021/jp0676181. Epub 2007 Mar 14. J Phys Chem B. 2007. PMID: 17388505 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yeagle, P. L. 1985. Cholesterol and the cell membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 822:267–287. - PubMed
-
- Papahadjopoulos, D., S. Nir, and S. Ohki. 1971. Permeability of phospholipid membranes: effect of cholesterol and temperature. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 266:561–583. - PubMed
-
- Corvera, E., O. G. Mouritsen, M. A. Singer, and M. J. Zuckermann. 1992. The permeability and the effect of acyl-chain length for phospholipid bilayers containing cholesterol: theory and experiment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1107:261–270. - PubMed
-
- Kraske, W. V., and D. B. Mountcastle. 2001. Effects of cholesterol and temperature on the permeability of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers near the chain melting phase transition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1514:159–164. - PubMed
-
- Kuo, A.-L., and C. G. Wade. 1979. Lipid lateral diffusion by pulsed nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 18:2300–2309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

