Alpha-fetoprotein triggers hepatoma cells escaping from immune surveillance through altering the expression of Fas/FasL and tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand and its receptor of lymphocytes and liver cancer cells
- PMID: 15849812
- PMCID: PMC4305744
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i17.2564
Alpha-fetoprotein triggers hepatoma cells escaping from immune surveillance through altering the expression of Fas/FasL and tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand and its receptor of lymphocytes and liver cancer cells
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the mechanism of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in escaping from the host immune surveillance of hepatocellular carcinoma.
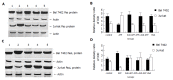
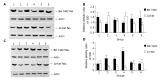
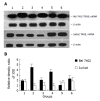
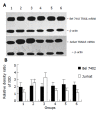
Methods: AFP purified from human umbilical blood was administrated into the cultured human lymphoma Jurkat T cell line or hepatoma cell line, Bel7402 in vitro. The expression of tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and its receptor (TRAILR) mRNA were analyzed by Northern blot and Western blot was used to detect the expression of Fas and Fas ligand (FasL) protein.
Results: AFP (20 mg/L) could promote the expression of FasL and TRAIL, and inhibit the expression of Fas and TRAILR of Bel7402 cells. For Jurkat cell line, AFP could suppress the expression of FasL and TRAIL, and stimulate the expression of Fas and TRAILR. AFP also could synergize with Bel7402 cells to inhibit the expression of FasL protein and TRAIL mRNA in Jurkat cells. The monoclonal antibody against AFP (anti-AFP) could abolish these functions of AFP.
Conclusion: AFP is able to promote the expression of FasL and TRAIL in hepatoma cells and enhance the expression of Fas and TRAILR in lymphocytes. These could elicit the escape of hepatocellular carcinoma cells from the host's lymphocytes immune surveillance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of alpha fetoprotein on escape of Bel 7402 cells from attack of lymphocytes.BMC Cancer. 2005 Aug 5;5:96. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-5-96. BMC Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16080799 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the apoptosis-inducing ligands FasL and TRAIL in malignant and benign human breast tumors.Histochem Cell Biol. 2000 Mar;113(3):189-94. doi: 10.1007/s004180050438. Histochem Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10817673
-
Conditionally replicative adenovirus vector carrying TRAIL gene for enhanced oncolysis of human hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Mol Med. 2005 Dec;16(6):1179-84. Int J Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 16273304
-
On the role and significance of Fas (Apo-1/CD95) ligand (FasL) expression in immune privileged tissues and cancer cells using multiple myeloma as a model.Leuk Lymphoma. 1998 Nov;31(5-6):477-90. doi: 10.3109/10428199809057607. Leuk Lymphoma. 1998. PMID: 9922038 Review.
-
Apoptosis induced by FasL and TRAIL/Apo2L in the pathogenesis of thyroid diseases.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2001 Nov;12(9):384-90. doi: 10.1016/s1043-2760(01)00441-6. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2001. PMID: 11595539 Review.
Cited by
-
Serum tumor markers for detection of hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Feb 28;12(8):1175-81. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i8.1175. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16534867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum alpha-fetoprotein levels during and after interferon therapy and the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis C.Dig Dis Sci. 2009 Nov;54(11):2530-7. doi: 10.1007/s10620-008-0642-y. Epub 2008 Dec 18. Dig Dis Sci. 2009. PMID: 19093203
-
Alpha fetoprotein antagonizes apoptosis induced by paclitaxel in hepatoma cells in vitro.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 3;6:26472. doi: 10.1038/srep26472. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27255186 Free PMC article.
-
AFP promotes HCC progression by suppressing the HuR-mediated Fas/FADD apoptotic pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Oct 2;11(10):822. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03030-7. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 33009373 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-fetoprotein accelerates the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting Bcl-2 gene expression through an RA-RAR signalling pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Dec;24(23):13804-13812. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15962. Epub 2020 Oct 22. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33090723 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parasole R, Izzo F, Perrone F, Pignata S, Galati MG, Leonardi E, Castiglione F, Orlando R, Castello G, Esposito G, et al. Prognostic value of serum biological markers in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:3504–3509. - PubMed
-
- Deutsch HF. Chemistry and biology of alpha-fetoprotein. Adv Cancer Res. 1991;56:253–312. - PubMed
-
- Dudich E, Semenkova L, Gorbatova E, Dudich I, Khromykh L, Tatulov E, Grechko G, Sukhikh G. Growth-regulative activity of human alpha-fetoprotein for different types of tumor and normal cells. Tumour Biol. 1998;19:30–40. - PubMed
-
- Wang XW, Xie H. Alpha-fetoprotein enhances the proliferation of human hepatoma cells in vitro. Life Sci. 1999;64:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Wang XW, Xu B. Stimulation of tumor-cell growth by alpha-fetoprotein. Int J Cancer. 1998;75:596–599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

