Construction, expression and characterization of human interferon alpha2b-(G4S)n-thymosin alpha1 fusion proteins in Pichia pastoris
- PMID: 15849818
- PMCID: PMC4305750
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i17.2597
Construction, expression and characterization of human interferon alpha2b-(G4S)n-thymosin alpha1 fusion proteins in Pichia pastoris
Abstract
Aim: Interferon alpha2b (IFNalpha2b) and thymosin alpha1 (Talpha1) exhibit synergic effects in the treatment of hepatitis B and hepatitis C when used together. For developing a fusion protein drug, fusion proteins of IFNalpha2b and Talpha1 linked by different lengths of (G4S)n (n = 1-3) were constructed and expressed in Pichia pastoris.
Methods: Using PCR and molecular clone techniques, the fusion genes of IFNalpha2b-(G4S)n-Talpha1 (n = 1-3) were constructed and subcloned into the eukaryotic expression vector pPIC9. After transformation of these plasmids into P. pastoris, the expressed fusion proteins IFNalpha2b-(G4S)n-Talpha1 (n = 1-3) were obtained. These proteins were purified through diethylaminoethyl (DEAE) affinity chromatography and Superdex 75 gel filtration and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blot. Antiviral and E-rosette assays were used to investigate the bioactivities of these fusion proteins.
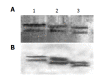
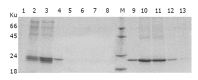
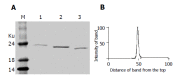
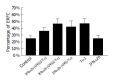
Results: DNA sequencing confirmed that the fusion genes of IFNalpha2b-(G4S)n-Talpha1 (n = 1-3) were correctly cloned to the pPIC9 vector. The recombinant IFNalpha2b-(G4S)n-Talpha1 (n = 1-3) fusion proteins expressed in P. pastoris were purified with DEAE and Superdex 75 gel filtration chromatography. The fusion proteins could be observed on sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with molecular weight (MW) of 23.2, 22.9, and 22.6 ku, respectively, and reacted to the IFNalpha2b monoclonal antibody and Talpha1 polyclonal antibody. The purified fusion proteins exhibit antiviral activity and can enhance the percentage of E-rosette-forming-cell in E-rosette assay.
Conclusion: The recombinant IFNalpha2b-(G4S)n-Talpha1 (n = 1-3) fusion proteins were successfully expressed in P. pastoris. Purified fusion proteins exhibit both antiviral activity of IFNalpha2b and immunomodulatory activity of Talpha1 in vitro. These results will be the basis for further evaluation of the fusion proteins' function in vivo.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Generation of mature Nα-terminal acetylated thymosin α 1 by cleavage of recombinant prothymosin α.ScientificWorldJournal. 2013 Oct 28;2013:387282. doi: 10.1155/2013/387282. eCollection 2013. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013. PMID: 24288480 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactivity and pharmacokinetics of two human serum albumin-thymosin alpha1-fusion proteins, rHSA-Talpha1 and rHSA-L-Talpha1, expressed in recombinant Pichia pastoris.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2010 Sep;59(9):1335-45. doi: 10.1007/s00262-010-0862-9. Epub 2010 May 16. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2010. PMID: 20473755 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of thymosin alpha1-thymopentin fusion peptide in Pichia pastoris and its characterization.Arch Pharm Res. 2008 Nov;31(11):1471-6. doi: 10.1007/s12272-001-2132-z. Epub 2008 Nov 21. Arch Pharm Res. 2008. PMID: 19023544
-
Thymosin α1 and Its Role in Viral Infectious Diseases: The Mechanism and Clinical Application.Molecules. 2023 Apr 17;28(8):3539. doi: 10.3390/molecules28083539. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37110771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymosin alpha1. SciClone Pharmaceuticals.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2002 May;3(5):698-707. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2002. PMID: 12090542 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression, purification and characterization of a novel soluble human thymosin alpha1 concatemer exhibited a stronger stimulation on mice lymphocytes proliferation and higher anti-tumor activity.Int J Biol Sci. 2011;7(5):618-28. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.7.618. Epub 2011 May 19. Int J Biol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21647330 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of mature Nα-terminal acetylated thymosin α 1 by cleavage of recombinant prothymosin α.ScientificWorldJournal. 2013 Oct 28;2013:387282. doi: 10.1155/2013/387282. eCollection 2013. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013. PMID: 24288480 Free PMC article.
-
Production of Nα-acetylated thymosin α1 in Escherichia coli.Microb Cell Fact. 2011 Apr 22;10:26. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-10-26. Microb Cell Fact. 2011. PMID: 21513520 Free PMC article.
-
Thymosin alpha 1: biological activities, applications and genetic engineering production.Peptides. 2010 Nov;31(11):2151-8. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2010.07.026. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Peptides. 2010. PMID: 20699109 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Di Bisceglie AM, Martin P, Lisker-Melman M, Kassianides C, Korenman J, Bergasa NV, Baker B, Hoofnagle JH. Therapy of chronic delta hepatitis with interferon alfa-2b. J Hepatol. 1990;11 Suppl 1:S151–S154. - PubMed
-
- Tamayo L, Ortiz DM, Orozco-Covarrubias L, Durán-McKinster C, Mora MA, Avila E, Teixeira F, Ruiz-Maldonado R. Therapeutic efficacy of interferon alfa-2b in infants with life-threatening giant hemangiomas. Arch Dermatol. 1997;133:1567–1571. - PubMed
-
- Romerio F, Zella D. MEK and ERK inhibitors enhance the anti-proliferative effect of interferon-alpha2b. FASEB J. 2002;16:1680–1682. - PubMed
-
- Ancell CD, Phipps J, Young L. Thymosin alpha-1. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2001;58:879–85; quiz 886-8. - PubMed
-
- Billich A. Thymosin alpha1. SciClone Pharmaceuticals. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2002;3:698–707. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

