Capability of multidetector CT to diagnose hepatocellular carcinoma-associated arterioportal shunt
- PMID: 15849831
- PMCID: PMC4305763
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i17.2666
Capability of multidetector CT to diagnose hepatocellular carcinoma-associated arterioportal shunt
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the capability of multidetector CT (MDCT) to diagnose HCC-associated arterioportal shunt (APS).
Methods: Two hundred and eighty-two patients with HCC received both thin-slice and enhancement MDCT scanning at early hepatic arterial phase, late hepatic arterial phase and portal venous phase, and digital subtract angiography (DSA) examination. Images were analyzed jointly by two experienced radiologists blinded to the opposite examination results, including the existence or not of APS, shunt locations, types and degrees of APS, with or without thrombosis.
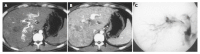
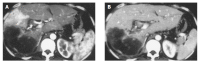
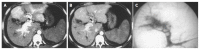
Results: There were 56 APS associated with HCC, including 48 central, seven peripheral and one mixed, or 42 severe, seven moderate, seven mild APS. Forty-one severe, seven moderate and central APS were all revealed with MDCT and DSA. Seven mild and peripheral APS were all displayed with MDCT; only five of them displayed DSA, two faint shunt APS associated with massive HCC were missed. One mixed APS was demonstrated as severe combined with mild shunt with both MDCT and DSA.
Conclusion: MDCT could diagnose not only DSA revealed APS, but also missed mild and peripheral APS with DSA due to faint shunt associated with massive HCC, is a simple, effective and noninvasive new technique for diagnosis of HCC-associated APS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Diagnostic capability of multidetector CT for arterioportal shunt in hepatocellular carcinoma].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2004 Apr;26(4):231-3. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15312387 Chinese.
-
Study on hepatocellular carcinoma-associated hepatic arteriovenous shunt using multidetector CT.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Nov;9(11):2455-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i11.2455. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 14606075 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Multidetector spiral CT findings of arteriovenous fistula associated with hepatocellular carcinoma].Ai Zheng. 2004 Jul;23(7):833-8. Ai Zheng. 2004. PMID: 15248923 Chinese.
-
Hepatic arterioportal shunts: dynamic CT and MR features.Korean J Radiol. 2002 Jan-Mar;3(1):1-15. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2002.3.1.1. Korean J Radiol. 2002. PMID: 11919473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Portal hypertension induced by congenital hepatic arterioportal fistula: report of four clinical cases and review of the literature.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Feb 21;21(7):2229-35. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i7.2229. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25717263 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with severe intratumoral arterioportal shunt.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Jul 7;16(25):3211-4. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i25.3211. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20593509 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical approach to multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis and arterioportal shunt leading to portal hypertension and bleeding: a case report.World J Surg Oncol. 2012 Feb 13;10:34. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-10-34. World J Surg Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22330617 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective study of TACE combined with sorafenib vs TACE combined with 125I seed implantation in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus and arterioportal fistulas.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 5;12:977462. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.977462. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36276129 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment efficacy and safety of drug-eluting beads transarterial chemoembolization versus conventional transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with arterioportal fistula.Cancer Biol Ther. 2022 Dec 31;23(1):89-95. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2021.2020059. Cancer Biol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35230928 Free PMC article.
-
Portal vein embolization: rationale, technique, and current application.Semin Intervent Radiol. 2012 Jun;29(2):81-9. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1312568. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2012. PMID: 23729977 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takahashi S, Murakami T, Takamura M, Kim T, Hori M, Narumi Y, Nakamura H, Kudo M. Multi-detector row helical CT angiography of hepatic vessels: depiction with dual-arterial phase acquisition during single breath hold. Radiology. 2002;222:81–88. - PubMed
-
- Mortele KJ, McTavish J, Ros PR. Current techniques of computed tomography. Helical CT, multidetector CT, and 3D reconstruction. Clin Liver Dis. 2002;6:29–52. - PubMed
-
- Chen JH, Chai JW, Huang CL, Hung HC, Shen WC, Lee SK. Proximal arterioportal shunting associated with hepatocellular carcinoma: features revealed by dynamic helical CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999;172:403–407. - PubMed
-
- Chen JH, Chen WP, Huang CL, Shen WC. Dynamic helical CT as a novel technique for diagnosing hepatic perfusion disorders. Hepatogastroenterology. 1999;46:303–307. - PubMed
-
- Chen JH, Huang CL, Hwang JI, Lee SK, Shen WC. Dynamic helical biphasic CT emerges as a potential tool for the diagnosis of proximal arterioportal shunting. Hepatogastroenterology. 1999;46:1791–1797. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

