A type I interferon autocrine-paracrine loop is involved in Toll-like receptor-induced interleukin-12p70 secretion by dendritic cells
- PMID: 15851485
- PMCID: PMC2213193
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20041964
A type I interferon autocrine-paracrine loop is involved in Toll-like receptor-induced interleukin-12p70 secretion by dendritic cells
Abstract
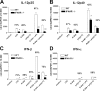
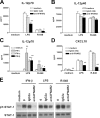
Dendritic cells (DC) produce interleukin-12 (IL-12) in response to Toll-like receptor (TLR) activation. Two major TLR signaling pathways participate in the response to pathogens: the nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB)-dependent pathway leading to inflammatory cytokine secretion including IL-12 and the interferon (IFN)-dependent pathway inducing type I IFN and IFN-regulated genes. Here we show that the two pathways cooperate and are likely both necessary for inducing an optimal response to pathogens. R-848/Resiquimod (TLR7 ligand in the mouse and TLR7/8 ligand in human) synergized with poly(I:C) (TLR3 ligand) or lipopolysaccharide (LPS; TLR4 ligand) in inducing high levels of bioactive IL-12p70 secretion and IFN-beta mRNA accumulation by mouse bone marrow-derived DC (BM-DC). Strikingly, IL-12p70 but not IL-12p40 secretion was strongly reduced in BM-DC from STAT1(-/-) and IFNAR(-/-) mice. STAT1 tyrosine-phosphorylation, IL-12p35, and IFN-beta mRNA accumulation were strongly inhibited in IFNAR(-/-) BM-DC activated with the TLR ligand combinations. Similar observation were obtained in human TLR8-expressing monocyte-derived DC (moDC) using neutralizing anti-IFNAR2 antibodies, although results also pointed to a possible involvement of IFN-lambda1 (also known as IL-29). This suggests that TLR engagement on DC induces endogenous IFNs that further synergize with the NF-kappaB pathway for optimal IL-12p70 secretion. Moreover, analysis of interferon regulatory factors (IRF) regulation in moDC suggests a role for IRF7/8 in mediating IRF3-independent type I IFN and possibly IL-12p35 synthesis in response to TLR7/8.
Figures





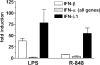

References
-
- Banchereau, J., and R.M. Steinman. 1998. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature. 392:245–252. - PubMed
-
- Janeway, C.A., Jr., and R. Medzhitov. 2002. Innate immune recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20:197–216. - PubMed
-
- Akira, S., K. Takeda, and T. Kaisho. 2001. Toll-like receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2:675–680. - PubMed
-
- Takeda, K., T. Kaisho, and S. Akira. 2003. Toll-like receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 21:335–376. - PubMed
-
- Dunne, A., and L.A. O'Neill. 2003. The interleukin-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily: signal transduction during inflammation and host defense. Sci. STKE. 2003:re3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

