The 3' end of the heavy chain constant region locus enhances germline transcription and switch recombination of the four gamma genes
- PMID: 15851486
- PMCID: PMC2213191
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20041988
The 3' end of the heavy chain constant region locus enhances germline transcription and switch recombination of the four gamma genes
Abstract
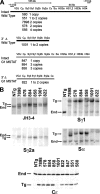
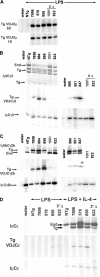
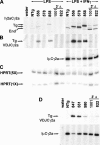
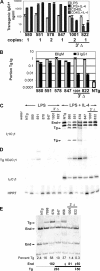
The switch in immunoglobulin (Ig) heavy chain class is preceded by germline transcription and then mediated by a DNA recombination event. To study germline transcription and class switch recombination we used transgenic mice with a 230-kilobase bacterial artificial chromosome that included a rearranged VDJ gene and the entire heavy chain constant region locus. In addition to several lines with intact transgenes, we identified two lines in which the heavy chain locus transgene lacked Calpha and everything 3' of it, including the regulatory elements HS3a, HS1-2, HS3b, and HS4. B cells from both lines with the truncated transgenes make abundant transgenic (Tg) VDJCmu transcripts and IgM protein. Deletion of the 3' end of the locus results in dramatically reduced expression of both germline transcripts and switched VDJCH transcripts of the gamma3, gamma2b, gamma2a, and epsilon genes. In addition, the transgenes lacking the 3' end of the locus express reduced amounts of gamma1 germline transcripts and 2-3% of the amount of Tg IgG1 in tissue culture compared with intact transgenes. Finally, switch recombination to gamma1 is undetectable in the transgenes lacking the 3' elements, as measured by digestion circularization-polymerase chain reaction or by the expression of VDJCgamma1 transcripts.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Germline transcription and switch recombination of a transgene containing the entire H chain constant region locus: effect of a mutation in a STAT6 binding site in the gamma 1 promoter.J Immunol. 2004 Nov 1;173(9):5531-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.9.5531. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15494502
-
Transgenes of the mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain locus, lacking distal elements in the 3' regulatory region, are impaired for class switch recombination.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55842. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055842. Epub 2013 Feb 8. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23409061 Free PMC article.
-
Germline transcription and recombination of a murine VDJmudeltagamma1 transgene.Int Immunol. 1998 Aug;10(8):1027-37. doi: 10.1093/intimm/10.8.1027. Int Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9723688
-
The molecular events in heavy chain class-switching.Semin Immunol. 1989 Sep;1(1):65-77. Semin Immunol. 1989. PMID: 15630960 Review.
-
Panorama of stepwise involvement of the IgH 3' regulatory region in murine B cells.Adv Immunol. 2021;149:95-114. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2021.03.004. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Adv Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33993921 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription factor Ebf1 regulates differentiation stage-specific signaling, proliferation, and survival of B cells.Genes Dev. 2012 Apr 1;26(7):668-82. doi: 10.1101/gad.187328.112. Epub 2012 Mar 19. Genes Dev. 2012. PMID: 22431510 Free PMC article.
-
Current insights into the mechanism of mammalian immunoglobulin class switch recombination.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2019 Aug;54(4):333-351. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2019.1659227. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31509023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Germline deletion of Igh 3' regulatory region elements hs 5, 6, 7 (hs5-7) affects B cell-specific regulation, rearrangement, and insulation of the Igh locus.J Immunol. 2012 Mar 15;188(6):2556-66. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102763. Epub 2012 Feb 17. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22345664 Free PMC article.
-
Switch recombination and somatic hypermutation are controlled by the heavy chain 3' enhancer region.J Exp Med. 2009 Nov 23;206(12):2613-23. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091280. Epub 2009 Nov 2. J Exp Med. 2009. PMID: 19887393 Free PMC article.
-
Activation-induced deaminase heterozygous MRL/lpr mice are delayed in the production of high-affinity pathogenic antibodies and in the development of lupus nephritis.Immunology. 2009 Jan;126(1):102-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02882.x. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Immunology. 2009. PMID: 18624728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manis, J.P., M. Tian, and F.W. Alt. 2003. Mechanism and control of class-switch recombination. Trends Immunol. 23:31–39. - PubMed
-
- Birshtein, B.K., C. Chen, S. Saleque, J.S. Michaelson, M. Singh, and R.D. Little. 1997. Murine and human 3′ IgH regulatory sequences. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 224:73–80. - PubMed
-
- Stavnezer, J. 2000. Molecular processes that regulate class-switching. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 245:127–168. - PubMed
-
- Giannini, S.L., M. Singh, C.-F. Calvo, G. Ding, and B.K. Birshtein. 1993. DNA regions flanking the mouse Ig 3′ α enhancer are differentially methylated and DNase I hypersensitive during B cell differentiation. J. Immunol. 150:1772–1780. - PubMed
-
- Madisen, L., and M. Groudine. 1994. Identification of a locus control region (LCR) in the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus that deregulates c-myc expression in plasmacytoma and Burkitt's lymphoma cells. Genes Dev. 8:2212–2226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

