LL5beta: a regulator of postsynaptic differentiation identified in a screen for synaptically enriched transcripts at the neuromuscular junction
- PMID: 15851520
- PMCID: PMC2171857
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200411012
LL5beta: a regulator of postsynaptic differentiation identified in a screen for synaptically enriched transcripts at the neuromuscular junction
Abstract
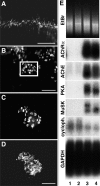
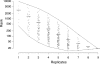
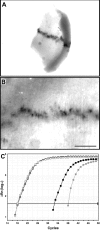
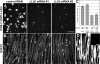
In both neurons and muscle fibers, specific mRNAs are concentrated beneath and locally translated at synaptic sites. At the skeletal neuromuscular junction, all synaptic RNAs identified to date encode synaptic components. Using microarrays, we compared RNAs in synapse-rich and -free regions of muscles, thereby identifying transcripts that are enriched near synapses and that encode soluble membrane and nuclear proteins. One gene product, LL5beta, binds to both phosphoinositides and a cytoskeletal protein, filamin, one form of which is concentrated at synaptic sites. LL5beta is itself associated with the cytoplasmic face of the postsynaptic membrane; its highest levels border regions of highest acetylcholine receptor (AChR) density, which suggests a role in "corraling" AChRs. Consistent with this idea, perturbing LL5beta expression in myotubes inhibits AChR aggregation. Thus, a strategy designed to identify novel synaptic components led to identification of a protein required for assembly of the postsynaptic apparatus.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

