Negative regulation of Toll-like receptor 4 signaling by the Toll-like receptor homolog RP105
- PMID: 15852007
- PMCID: PMC2144914
- DOI: 10.1038/ni1198
Negative regulation of Toll-like receptor 4 signaling by the Toll-like receptor homolog RP105
Abstract
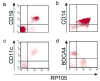
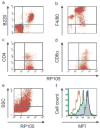
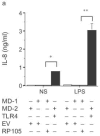
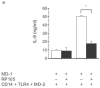
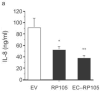
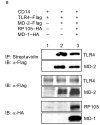
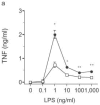
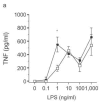
Activation of Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling by microbial signatures is critical to the induction of immune responses. Such responses demand tight regulation. RP105 is a TLR homolog thought to be mostly B cell specific, lacking a signaling domain. We report here that RP105 expression was wide, directly mirroring that of TLR4 on antigen-presenting cells. Moreover, RP105 was a specific inhibitor of TLR4 signaling in HEK 293 cells, a function conferred by its extracellular domain. Notably, RP105 and its helper molecule, MD-1, interacted directly with the TLR4 signaling complex, inhibiting its ability to bind microbial ligand. Finally, RP105 regulated TLR4 signaling in dendritic cells as well as endotoxin responses in vivo. Thus, our results identify RP105 as a physiological negative regulator of TLR4 responses.
Figures













References
-
- Medzhitov R, Janeway C., Jr Innate immune recognition: mechanisms and pathways. Immunol Rev. 2000;173:89–97. - PubMed
-
- Takeda K, Kaisho T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:335–76. - PubMed
-
- Beutler B, Rietschel ET. Innate immune sensing and its roots: the story of endotoxin. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:169–76. - PubMed
-
- Ardizzone S, Porro GB. Inflammatory bowel disease: new insights into pathogenesis and treatment. J Intern Med. 2002;252:475–96. - PubMed
-
- Bingham CO., 3rd The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: pivotal cytokines involved in bone degradation inflammation. J Rheumatol Suppl. 2002;65:3–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
