Ceramide upregulation causes pulmonary cell apoptosis and emphysema-like disease in mice
- PMID: 15852018
- PMCID: PMC1352344
- DOI: 10.1038/nm1238
Ceramide upregulation causes pulmonary cell apoptosis and emphysema-like disease in mice
Abstract
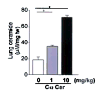
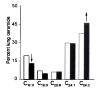
Alveolar cell apoptosis is involved in the pathogenesis of emphysema, a prevalent disease primarily caused by cigarette smoking. We report that ceramide, a second messenger lipid, is a crucial mediator of alveolar destruction in emphysema. Inhibition of enzymes controlling de novo ceramide synthesis prevented alveolar cell apoptosis, oxidative stress and emphysema caused by blockade of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors in both rats and mice. Emphysema was reproduced with intratracheal instillation of ceramide in naive mice. Excessive ceramide triggers a feed-forward mechanism mediated by activation of secretory acid sphingomyelinase, as suggested by experiments with neutralizing ceramide antibody in mice and with acid sphingomyelinase-deficient fibroblasts. Concomitant augmentation of signaling initiated by a prosurvival metabolite, sphingosine-1-phosphate, prevented lung apoptosis, implying that a balance between ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate is required for maintenance of alveolar septal integrity. Finally, increased lung ceramides in individuals with smoking-induced emphysema suggests that ceramide upregulation may be a crucial pathogenic element and a promising target in this disease that currently lacks effective therapies.
Figures





















Comment in
-
Lipid let loose in pulmonary emphysema.Nat Med. 2005 May;11(5):471-2. doi: 10.1038/nm0505-471. Nat Med. 2005. PMID: 15875047 No abstract available.
References
-
- The definition of emphysema. Report of a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Division of Lung Diseases workshop. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985;132:182–5. - PubMed
-
- Tuder RM, Petrache I, Elias JA, Voelkel NF, Henson PM. Apoptosis and emphysema: the missing link. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003;28:551–4. - PubMed
-
- Tuder RM, et al. Oxidative stress and apoptosis interact and cause emphysema due to vascular endothelial growth factor receptor blockade. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003;29:88–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

