Diabetes-induced changes in the 5-hydroxytryptamine inhibitory receptors involved in the pressor effect elicited by sympathetic stimulation in the pithed rat
- PMID: 15852039
- PMCID: PMC1576173
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706216
Diabetes-induced changes in the 5-hydroxytryptamine inhibitory receptors involved in the pressor effect elicited by sympathetic stimulation in the pithed rat
Abstract
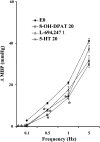
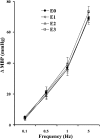
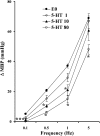
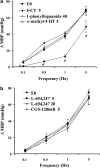
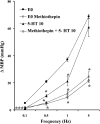
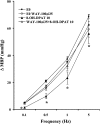
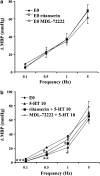
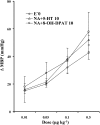
1. We investigated the effect of alloxan-induced diabetes on the inhibitory mechanisms of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) in the pressor responses induced by stimulation of sympathetic vasopressor outflow in pithed rats, and analysed the type and/or subtype of 5-HT receptors involved. 2. Diabetes was induced in male Wistar rats by a single s.c. injection of alloxan, then 4 weeks later, they were anaesthetized, pretreated with atropine and pithed. Electrical stimulation of the sympathetic outflow from the spinal cord (0.1, 0.5, 1 and 5 Hz) resulted in frequency-dependent increases in blood pressure. 3. Intravenous infusions of 5-HT (1-80 microg kg(-1) min(-1)) reduced the pressor effects obtained by electrical stimulation. The 5-HT(1) receptor agonist 5-carboxamidotryptamine, 5-CT (5 microg kg(-1) min(-1)), caused an inhibition of the pressor response, whereas the selective 5-HT(2) receptor agonist, alpha-methyl-5-HT (5 microg kg(-1) min(-1)) and the selective 5-HT(3) receptor agonist, 1-phenylbiguanide (40 microg kg(-1) min(-1)), did not modify the sympathetic pressor responses. 5-HT had no effect on exogenous noradrenaline (NA)-induced pressor responses. 4. The inhibition of electrically induced pressor responses by 5-HT (10 microg kg(-1) min(-1)) was unable to be elicited after i.v. treatment with methiothepin (100 microg kg(-1)) because of the marked inhibition produced by methiothepin alone. The 5-HT-induced inhibition was blocked after i.v. administration of WAY-100,635 (100 microg kg(-1)) and not affected by ritanserin (1 mg kg(-1)), MDL 72222 (2 mg kg(-1)). 5. The selective 5-HT(1A) receptor agonist, 8-hydroxydipropylaminotretalin hydrobromide (8-OH-DPAT) (5-20 microg kg(-1) min(-1)) but neither the rodent 5-HT(1B) receptor agonist, CGS-12066B (5 microg kg(-1) min(-1)), nor the selective nonrodent 5-HT(1B) and 5-HT(1D) receptor agonist, L-694,247 (5 and 40 microg kg(-1) min(-1)), inhibited the electrically induced pressor response. The selective 5-HT(1A) receptor antagonist, WAY-100,635 (100 microg kg(-1)), blocked the inhibition induced by 8-OH-DPAT (10 microg kg(-1) min(-1)). 8-OH-DPAT had no effect on exogenous NA-induced pressor responses. 6. Experimental diabetes produces changes in the inhibitory effect induced by 5-HT on electrically induced sympathetic pressor responses, such that the inhibitory action induced by 5-HT in diabetic pithed rats is mediated by prejunctional 5-HT(1A) receptors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pharmacological profile of 5-hydroxytryptamine-induced inhibition on the pressor effect elicited by sympathetic stimulation in long-term diabetic pithed rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2010 Sep 15;643(1):70-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.06.013. Epub 2010 Jun 12. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20547148
-
Diabetes-induced changes in 5-hydroxytryptamine modulation of vagally-induced bradycardia in rat heart.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007 Nov;34(11):1199-206. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2007.04688.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17880377
-
Characterization of prejunctional 5-HT1 receptors that mediate the inhibition of pressor effects elicited by sympathetic stimulation in the pithed rat.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Mar;123(6):1205-13. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701714. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9559906 Free PMC article.
-
[Role of serotonin receptors in vascular tone in the pithed rat].Arch Cardiol Mex. 2009 Dec;79 Suppl 2:83-94. Arch Cardiol Mex. 2009. PMID: 20361490 Review. Spanish.
-
Serotonin and blood pressure regulation.Pharmacol Rev. 2012 Apr;64(2):359-88. doi: 10.1124/pr.111.004697. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Pharmacol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22407614 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Renal Sympathetic Hyperactivity in Diabetes Is Modulated by 5-HT1D Receptor Activation via NO Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 10;24(2):1378. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021378. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674892 Free PMC article.
-
Role of peripheral 5-HT5A receptors in 5-HT-induced cardiac sympatho-inhibition in type 1 diabetic rats.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 9;10(1):19358. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76298-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33168874 Free PMC article.
-
5-Hydroxytryptamine does not reduce sympathetic nerve activity or neuroeffector function in the splanchnic circulation.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 May 5;754:140-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.02.032. Epub 2015 Feb 28. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25732865 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AGRAWAL D.K., BHIMJI S., MCNEILL J.H. Effect of chronic experimental diabetes on vascular smooth muscle function in rabbit carotid artery. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1987;9:584–593. - PubMed
-
- ANDERSSON D., BRUNKWALL J., BERGQVIST D., EDVINSSON E. Diminished contractile responses to neuropeptide Y of arteries from diabetic rats. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 1992;37:215–222. - PubMed
-
- AWOUTERS F., NIEMEGEERS C.J.E., MEGENS A.A.H.P., MEERT T.F., JANSSEN P.A.J. The pharmacological profile of ritanserin, very specific serotonin S2 antagonist. Drug Develop. Res. 1988;15:61–73.
-
- BAXTER G., KENNETT G., BLANEY F., BLACKBURN T. 5-HT2 receptor subtypes: a family reunited. TIPs. 1995;16:105–110. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

