Time course study of oxidative and nitrosative stress and antioxidant enzymes in K2Cr2O7-induced nephrotoxicity
- PMID: 15854231
- PMCID: PMC1142323
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2369-6-4
Time course study of oxidative and nitrosative stress and antioxidant enzymes in K2Cr2O7-induced nephrotoxicity
Abstract
Background: Potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7)-induced nephrotoxicity is associated with oxidative and nitrosative stress. In this study we investigated the relation between the time course of the oxidative and nitrosative stress with kidney damage and alterations in the following antioxidant enzymes: Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase (Cu, Zn-SOD), Mn-SOD, glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione reductase (GR), and catalase (CAT).
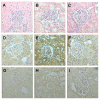
Methods: Nephrotoxicity was induced in rats by a single injection of K2Cr2O7. Groups of animals were sacrificed on days 1,2,3,4,6,8,10, and 12. Nephrotoxicity was evaluated by histological studies and by measuring creatinine clearance, serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and urinary excretion of N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase (NAG) and total protein. Oxidative and nitrosative stress were measured by immunohistochemical localization of protein carbonyls and 3-nitrotyrosine, respectively. Cu, Zn-SOD, Mn-SOD, and CAT were studied by immunohistochemical localization. The activity of total SOD, CAT, GPx, and GR was also measured as well as serum and kidney content of chromium and urinary excretion of NO2 -/NO3-. Data were compared by two-way analysis of variance followed by a post hoc test.
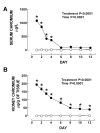
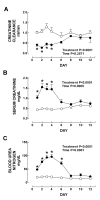
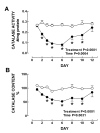
Results: Serum and kidney chromium content increased reaching the highest value on day 1. Nephrotoxicity was made evident by the decrease in creatinine clearance (days 1-4) and by the increase in serum creatinine (days 1-4), BUN (days 1-6), urinary excretion of NAG (days 1-4), and total protein (day 1-6) and by the structural damage to the proximal tubules (days 1-6). Oxidative and nitrosative stress were clearly evident on days 1-8. Urinary excretion of NO2-/NO3- decreased on days 2-6. Mn-SOD and Cu, Zn-SOD, estimated by immunohistochemistry, and total SOD activity remained unchanged. Activity of GPx decreased on days 3-12 and those of GR and CAT on days 2-10. Similar findings were observed by immunohistochemistry of CAT.
Conclusion: These data show the association between oxidative and nitrosative stress with functional and structural renal damage induced by K2Cr2O7. Renal antioxidant enzymes were regulated differentially and were not closely associated with oxidative or nitrosative stress or with kidney damage. In addition, the decrease in the urinary excretion of NO2-/NO3- was associated with the renal nitrosative stress suggesting that nitric oxide was derived to the formation of reactive nitrogen species involved in protein nitration.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Hypothyroidism attenuates protein tyrosine nitration, oxidative stress and renal damage induced by ischemia and reperfusion: effect unrelated to antioxidant enzymes activities.BMC Nephrol. 2005 Nov 7;6:12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-6-12. BMC Nephrol. 2005. PMID: 16274486 Free PMC article.
-
Deferoxamine pretreatment prevents Cr(VI)-induced nephrotoxicity and oxidant stress: role of Cr(VI) chelation.Toxicology. 2012 Jan 27;291(1-3):93-101. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2011.11.003. Epub 2011 Nov 15. Toxicology. 2012. PMID: 22115772
-
Protective effect of ebselen, a selenoorganic drug, against gentamicin-induced renal damage in rats.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2006 Sep;99(3):267-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2006.pto_474.x. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2006. PMID: 16930301
-
[Indicators of oxidative stress in cardiovascular diseases. II. Nitrogenous substances, AGE-substances and antioxidants].Vnitr Lek. 1999 Jun;45(6):373-8. Vnitr Lek. 1999. PMID: 11045175 Review. Czech.
-
[The role of oxidative metabolite enzymes in oxidative stress induced by exogenous chemicals].Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2014 Jul;32(7):549-54. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25182834 Review. Chinese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Comparison of kidney injury molecule-1 and other nephrotoxicity biomarkers in urine and kidney following acute exposure to gentamicin, mercury, and chromium.Toxicol Sci. 2008 Jan;101(1):159-70. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfm260. Epub 2007 Oct 13. Toxicol Sci. 2008. PMID: 17934191 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothyroidism attenuates protein tyrosine nitration, oxidative stress and renal damage induced by ischemia and reperfusion: effect unrelated to antioxidant enzymes activities.BMC Nephrol. 2005 Nov 7;6:12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-6-12. BMC Nephrol. 2005. PMID: 16274486 Free PMC article.
-
An evaluation of the protective role of vitamin C in reactive oxygen species-induced hepatotoxicity due to hexavalent chromium in vitro and in vivo.J Occup Med Toxicol. 2017 Jun 15;12:15. doi: 10.1186/s12995-017-0161-x. eCollection 2017. J Occup Med Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28638434 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin pretreatment prevents potassium dichromate-induced hepatotoxicity, oxidative stress, decreased respiratory complex I activity, and membrane permeability transition pore opening.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:424692. doi: 10.1155/2013/424692. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23956771 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Pre-Diagnostic Metabolic Patterns for Glioma Using Subset Analysis of Matched Repeated Time Points.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Nov 12;12(11):3349. doi: 10.3390/cancers12113349. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33198241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ingber A, Gammelgaard B, David M. Detergents and bleaches are sources of chromium contact dermatitis in Israel. Contact Dermatitis. 1998;38:101–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

