The transcription factor Gli3 regulates differentiation of fetal CD4- CD8- double-negative thymocytes
- PMID: 15855276
- PMCID: PMC1274277
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-03-0998
The transcription factor Gli3 regulates differentiation of fetal CD4- CD8- double-negative thymocytes
Abstract
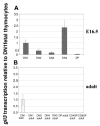
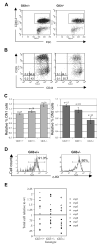
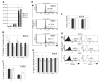
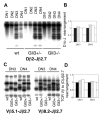
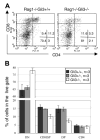
Glioblastoma 3 (Gli3) is a transcription factor involved in patterning and oncogenesis. Here, we demonstrate a role for Gli3 in thymocyte development. Gli3 is differentially expressed in fetal CD4- CD8- double-negative (DN) thymocytes and is most highly expressed at the CD44+ CD25- DN (DN1) and CD44- CD25- (DN4) stages of development but was not detected in adult thymocytes. Analysis of null mutants showed that Gli3 is involved at the transitions from DN1 to CD44+ CD25+ DN (DN2) cell and from DN to CD4+ CD8+ double-positive (DP) cell. Gli3 is required for differentiation from DN to DP thymocyte, after pre-T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling but is not necessary for pre-TCR-induced proliferation or survival. The effect of Gli3 was dose dependent, suggesting its direct involvement in the transcriptional regulation of genes controlling T-cell differentiation during fetal development.
Figures
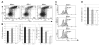
Similar articles
-
The Gli3 transcription factor expressed in the thymus stroma controls thymocyte negative selection via Hedgehog-dependent and -independent mechanisms.J Immunol. 2009 Sep 1;183(5):3023-32. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900152. Epub 2009 Aug 10. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19667090
-
Direct BMP2/4 signaling through BMP receptor IA regulates fetal thymocyte progenitor homeostasis and differentiation to CD4+CD8+ double-positive cell.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(2):324-33. doi: 10.4161/cc.27118. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24240189 Free PMC article.
-
Early growth response gene 3 regulates thymocyte proliferation during the transition from CD4-CD8- to CD4+CD8+.J Immunol. 2004 Jan 15;172(2):964-71. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.2.964. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14707069
-
Fc gamma RII/III and CD2 expression mark distinct subpopulations of immature CD4-CD8- murine thymocytes: in vivo developmental kinetics and T cell receptor beta chain rearrangement status.J Exp Med. 1993 Apr 1;177(4):1079-92. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.4.1079. J Exp Med. 1993. PMID: 8096236 Free PMC article.
-
NKT Cells in Mice Originate from Cytoplasmic CD3-Positive, CD4-CD8- Double-Negative Thymocytes that Express CD44 and IL-7Rα.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 12;9(1):1874. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37811-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30755654 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
GLI3: a mediator of genetic diseases, development and cancer.Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Apr 3;18(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00540-x. Cell Commun Signal. 2020. PMID: 32245491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stromal Gli signaling regulates the activity and differentiation of prostate stem and progenitor cells.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jul 6;293(27):10547-10560. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003255. Epub 2018 May 17. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29773652 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue-derived hedgehog proteins modulate Th differentiation and disease.J Immunol. 2013 Mar 15;190(6):2641-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202541. Epub 2013 Feb 13. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23408837 Free PMC article.
-
Non-redundant role for the transcription factor Gli1 at multiple stages of thymocyte development.Cell Cycle. 2010 Oct 15;9(20):4144-52. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.20.13453. Epub 2010 Oct 27. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20935514 Free PMC article.
-
Glioma-associated oncogene homologue 3, a hedgehog transcription factor, is highly expressed in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells of classical Hodgkin lymphoma.Hum Pathol. 2011 Nov;42(11):1643-52. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2010.12.023. Epub 2011 Apr 29. Hum Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21531006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rothenberg EV. T-lineage specification and commitment: a gene regulation perspective. Semin Immunol. 2002;14:431–440. - PubMed
-
- Michie AM, Zuniga-Pflucker JC. Regulation of thymocyte differentiation: pre-TCR signals and beta-selection. Semin Immunol. 2002;14:311–323. - PubMed
-
- Matise MP, Joyner AL. Gli genes in development and cancer. Oncogene. 1999;18:7852–7859. - PubMed
-
- Koebernick K, Pieler T. Gli-type zinc finger proteins as bipotential transducers of Hedgehog signaling. Differentiation. 2002;70:69–76. - PubMed
-
- Ingham PW, McMahon AP. Hedgehog signaling in animal development: paradigms and principles. Genes Dev. 2001;15:3059–3087. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

