The transcription factor Gli3 regulates differentiation of fetal CD4- CD8- double-negative thymocytes
- PMID: 15855276
- PMCID: PMC1274277
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-03-0998
The transcription factor Gli3 regulates differentiation of fetal CD4- CD8- double-negative thymocytes
Abstract
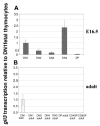
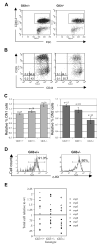
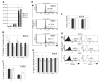
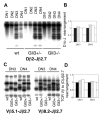
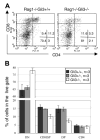
Glioblastoma 3 (Gli3) is a transcription factor involved in patterning and oncogenesis. Here, we demonstrate a role for Gli3 in thymocyte development. Gli3 is differentially expressed in fetal CD4- CD8- double-negative (DN) thymocytes and is most highly expressed at the CD44+ CD25- DN (DN1) and CD44- CD25- (DN4) stages of development but was not detected in adult thymocytes. Analysis of null mutants showed that Gli3 is involved at the transitions from DN1 to CD44+ CD25+ DN (DN2) cell and from DN to CD4+ CD8+ double-positive (DP) cell. Gli3 is required for differentiation from DN to DP thymocyte, after pre-T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling but is not necessary for pre-TCR-induced proliferation or survival. The effect of Gli3 was dose dependent, suggesting its direct involvement in the transcriptional regulation of genes controlling T-cell differentiation during fetal development.
Figures
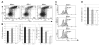
References
-
- Rothenberg EV. T-lineage specification and commitment: a gene regulation perspective. Semin Immunol. 2002;14:431–440. - PubMed
-
- Michie AM, Zuniga-Pflucker JC. Regulation of thymocyte differentiation: pre-TCR signals and beta-selection. Semin Immunol. 2002;14:311–323. - PubMed
-
- Matise MP, Joyner AL. Gli genes in development and cancer. Oncogene. 1999;18:7852–7859. - PubMed
-
- Koebernick K, Pieler T. Gli-type zinc finger proteins as bipotential transducers of Hedgehog signaling. Differentiation. 2002;70:69–76. - PubMed
-
- Ingham PW, McMahon AP. Hedgehog signaling in animal development: paradigms and principles. Genes Dev. 2001;15:3059–3087. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

