Inhibitory effect of aureobasidin A on Toxoplasma gondii
- PMID: 15855498
- PMCID: PMC1087623
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.49.5.1794-1801.2005
Inhibitory effect of aureobasidin A on Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
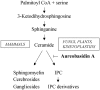
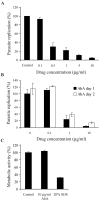
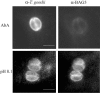
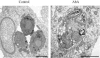
The apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii is a leading opportunistic pathogen associated with AIDS and congenital birth defects. Due to the need for identifying new parasite-specific treatments, the possibility of targeting sphingolipid biosynthesis in the parasite was investigated. Aureobasidin A, an inhibitor of the enzyme synthesizing the sphingolipid inositol phosphorylceramide, which is present in fungi, plants, and some protozoa but absent in mammalian cells, was found to block in vitro T. gondii replication without affecting host cell metabolism. Aureobasidin A treatment did not induce tachyzoite to bradyzoite stage conversion in T. gondii but resulted in a loss of intracellular structures and vacuolization within the parasite. In addition, aureobasidin A inhibited sphingolipid synthesis in T. gondii. Sphingolipid biosynthetic pathways may therefore be considered targets for the development of anti-T. gondii agents.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The antifungal Aureobasidin A and an analogue are active against the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii but do not inhibit sphingolipid biosynthesis.Parasitology. 2018 Feb;145(2):148-155. doi: 10.1017/S0031182017000506. Epub 2017 May 10. Parasitology. 2018. PMID: 28486997 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingolipid synthesis and scavenging in the intracellular apicomplexan parasite, Toxoplasma gondii.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2013 Jan;187(1):43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2012.11.007. Epub 2012 Dec 16. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 23246819 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma gondii in primary rat CNS cells: differential contribution of neurons, astrocytes, and microglial cells for the intracerebral development and stage differentiation.Exp Parasitol. 1999 Sep;93(1):23-32. doi: 10.1006/expr.1999.4421. Exp Parasitol. 1999. PMID: 10464035
-
Stress-related and spontaneous stage differentiation of Toxoplasma gondii.Mol Biosyst. 2008 Aug;4(8):824-34. doi: 10.1039/b800520f. Epub 2008 Jun 2. Mol Biosyst. 2008. PMID: 18633484 Review.
-
Lipid biology of Apicomplexa: perspectives for new drug targets, particularly for Toxoplasma gondii.Trends Parasitol. 2006 Jan;22(1):41-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2005.11.001. Epub 2005 Nov 21. Trends Parasitol. 2006. PMID: 16300997 Review.
Cited by
-
Toxoplasma gondii salvages sphingolipids from the host Golgi through the rerouting of selected Rab vesicles to the parasitophorous vacuole.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Jun;24(12):1974-95. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-11-0827. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23615442 Free PMC article.
-
Everybody needs sphingolipids, right! Mining for new drug targets in protozoan sphingolipid biosynthesis.Parasitology. 2018 Feb;145(2):134-147. doi: 10.1017/S0031182017001081. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Parasitology. 2018. PMID: 28637533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
De novo sphingolipid synthesis is essential for viability, but not for transport of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins, in African trypanosomes.Eukaryot Cell. 2007 Mar;6(3):454-64. doi: 10.1128/EC.00283-06. Epub 2007 Jan 12. Eukaryot Cell. 2007. PMID: 17220466 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of a Niemann-Pick, type C1-related protein in toxoplasma is associated with multiple lipidoses and increased pathogenicity.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Dec;7(12):e1002410. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002410. Epub 2011 Dec 8. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 22174676 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid synthesis in protozoan parasites: a comparison between kinetoplastids and apicomplexans.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):488-512. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.06.003. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23827884 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aspinall, T. V., D. H. Joynson, E. Guy, J. E. Hyde, and P. F. Sims. 2002. The molecular basis of sulfonamide resistance in Toxoplasma gondii and implications for the clinical management of toxoplasmosis. J. Infect. Dis. 185:1637-1643. - PubMed
-
- Azzouz, N., B. Rauscher, P. Gerold, M. F. Cesbron-Delauw, J. F. Dubremetz, and R. T. Schwarz. 2002. Evidence for de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis in Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 32:677-684. - PubMed
-
- Bligh, E. G., and W. J. Dyer. 1959. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Med. Sci. 37:911-917. - PubMed
-
- Campbell, S. A., T. A. Richards, E. J. Mui, B. U. Samuel, J. R. Coggins, R. McLeod, and C. W. Roberts. 2004. A complete shikimate pathway in Toxoplasma gondii: an ancient eukaryotic innovation. Int. J. Parasitol. 34:5-13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

