Induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in alveolar epithelial cells by transforming growth factor-beta1: potential role in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 15855634
- PMCID: PMC1606388
- DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)62351-6
Induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in alveolar epithelial cells by transforming growth factor-beta1: potential role in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
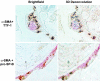
The hallmark of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is the myofibroblast, the cellular origin of which in the lung is unknown. We hypothesized that alveolar epithelial cells (AECs) may serve as a source of myofibroblasts through epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Effects of chronic exposure to transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1 on the phenotype of isolated rat AECs in primary culture and a rat type II cell line (RLE-6TN) were evaluated. Additionally, tissue samples from patients with IPF were evaluated for cells co-expressing epithelial (thyroid transcription factor (TTF)-1 and pro-surfactant protein-B (pro-SP-B), and mesenchymal (alpha-smooth muscle actin (alpha-SMA)) markers. RLE-6TN cells exposed to TGF-beta1 for 6 days demonstrated increased expression of mesenchymal cell markers and a fibroblast-like morphology, an effect augmented by tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). Exposure of rat AECs to TGF-beta1 (100 pmol/L) resulted in increased expression of alpha-SMA, type I collagen, vimentin, and desmin, with concurrent transition to a fibroblast-like morphology and decreased expression of TTF-1, aquaporin-5 (AQP5), zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), and cytokeratins. Cells co-expressing epithelial markers and alpha-SMA were abundant in lung tissue from IPF patients. These results suggest that AECs undergo EMT when chronically exposed to TGF-beta1, raising the possibility that epithelial cells may serve as a novel source of myofibroblasts in IPF.
Figures


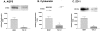



References
-
- Crystal RG, Bitterman PB, Mossman B, Schwarz MI, Sheppard D, Almasy L, Chapman HA, Friedman SL, King TE, Jr, Leinwand LA, Liotta L, Martin GR, Schwartz DM, Schultz GS, Wagner CR, Musson RA. Future research directions in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2002;166:236–246. - PubMed
-
- Travis WD, King TE, Jr, Bateman ED, Lynch DA. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society international multidisciplinary consensus classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Resp Crit Care Med. 2002;265:277–304. - PubMed
-
- Selman M, Pardo A. The epithelial/fibroblastic pathway in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003;29:S93–S96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

