Kinetics of disease progression and host response in a rat model of bubonic plague
- PMID: 15855643
- PMCID: PMC1606397
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62360-7
Kinetics of disease progression and host response in a rat model of bubonic plague
Abstract
Plague, caused by the gram-negative bacterium Yersinia pestis, primarily affects rodents but is also an important zoonotic disease of humans. Bubonic plague in humans follows transmission by infected fleas and is characterized by an acute, necrotizing lymphadenitis in the regional lymph nodes that drain the intradermal flea bite site. Septicemia rapidly follows with spread to spleen, liver, and other organs. We developed a model of bubonic plague using the inbred Brown Norway strain of Rattus norvegicus to characterize the progression and kinetics of infection and the host immune response after intradermal inoculation of Y. pestis. The clinical signs and pathology in the rat closely resembled descriptions of human bubonic plague. The bacteriology; histopathology; host cellular response in infected lymph nodes, blood, and spleen; and serum cytokine levels were analyzed at various times after infection to determine the kinetics and route of disease progression and to evaluate hypothesized Y. pestis pathogenic mechanisms. Understanding disease progression in this rat infection model should facilitate further investigations into the molecular pathogenesis of bubonic plague and the immune response to Y. pestis at different stages of the disease.
Figures
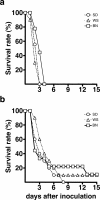






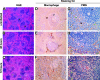

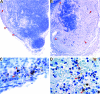
References
-
- Pollitzer R. Geneva: World Health Organization,; Plague. 1954
-
- Butler T. Plague and Other Yersinia Infections. New York: Plenum Press,; 1983
-
- Crowell BC. Pathologic anatomy of bubonic plague. Philipp J Sci. 1915;10:249–306.
-
- Flexner S. The pathology of bubonic plague. Am J Med Sci. 1901;122:396–416.
-
- Donavan JE, Ham D, Fukui GM, Surgalla MJ. Role of the capsule of Pasteurella pestis in bubonic plague in the guinea pig. J Infect Dis. 1961;109:154–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

