New antiviral pathway that mediates hepatitis C virus replicon interferon sensitivity through ADAR1
- PMID: 15858013
- PMCID: PMC1091666
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.10.6291-6298.2005
New antiviral pathway that mediates hepatitis C virus replicon interferon sensitivity through ADAR1
Abstract
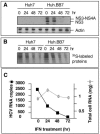
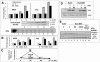
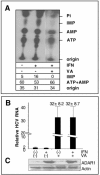
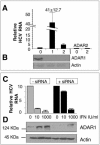
While many clinical hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections are resistant to alpha interferon (IFN-alpha) therapy, subgenomic in vitro self-replicating HCV RNAs (HCV replicons) are characterized by marked IFN-alpha sensitivity. IFN-alpha treatment of replicon-containing cells results in a rapid loss of viral RNA via translation inhibition through double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase (PKR) and also through a new pathway involving RNA editing by an adenosine deaminase that acts on double-stranded RNA (ADAR1). More than 200 genes are induced by IFN-alpha, and yet only a few are attributed with an antiviral role. We show that inhibition of both PKR and ADAR1 by the addition of adenovirus-associated RNA stimulates replicon expression and reduces the amount of inosine recovered from RNA in replicon cells. Small inhibitory RNA, specific for ADAR1, stimulated the replicon 40-fold, indicating that ADAR1 has a role in limiting replication of the viral RNA. This is the first report of ADAR's involvement in a potent antiviral pathway and its action to specifically eliminate HCV RNA through adenosine to inosine editing. These results may explain successful HCV replicon clearance by IFN-alpha in vitro and may provide a promising new therapeutic strategy for HCV as well as other viral infections.
Figures



References
-
- Bass, B. L. 1997. RNA editing and hypermutation by adenosine deamination. Trends Biochem. Sci. 22:157-162. - PubMed
-
- Blight, K. J., A. A. Kolykhalov, and C. M. Rice. 2000. Efficient initiation of HCV RNA replication in cell culture. Science 290:1972-1974. - PubMed
-
- Foy, E., K. Li, C. Wang, R. Sumpter, Jr., M. Ikeda, S. M. Lemon, and M. J. Gale. 2003. Regulation of interferon regulatory factor-3 by the hepatitis C virus serine protease. Science 300:1145-1148. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

