Tamoxifen resistance and Her2/neu expression in an aged, irradiated rat breast carcinoma model
- PMID: 15860508
- PMCID: PMC1224736
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgi103
Tamoxifen resistance and Her2/neu expression in an aged, irradiated rat breast carcinoma model
Abstract
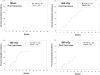
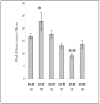
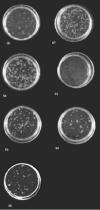
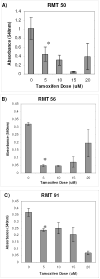
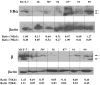
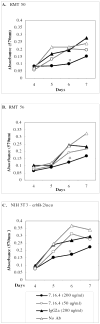
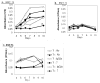
Clear links have been established between occupational or therapeutic radiation exposure and breast cancer. Tamoxifen chemoprevention following radiation exposure may be able to reduce the risk of developing breast cancer later in life. In order to model carcinogenesis in this setting, an in vivo model of tamoxifen chemoprevention and tamoxifen failure in a radiation-induced rat mammary carcinoma model was characterized. Two hundred and twenty-seven 60-day-old female rats received whole body or sham exposure to ionizing radiation. Thirty days later long-term, continuous, tamoxifen chemoprevention was initiated in half the population and all animals were monitored over three and a half years for the development of mammary tumors. Mammary tumors were surgically removed and carcinomas were histologically identified and characterized. Results showed that tamoxifen chemoprevention decreased the incidence and prolonged the latency of radiation-induced mammary carcinomas. However, many individuals receiving tamoxifen chemoprevention developed their first carcinoma very late in life. These carcinomas shared morphological features distinct from the majority of carcinomas that developed in the absence of tamoxifen chemoprevention. Analyses of cell lines established from these carcinomas and immunohistochemistry of tumor sections revealed that the highest levels of Her2/neu expression were associated with in vivo tamoxifen exposure. Treatment of rat mammary carcinoma cells with an anti-rat Her2/neu monoclonal antibody (MAb 7.16.4) inhibited cell growth and this effect was more pronounced in the presence of tamoxifen. These studies suggest that carcinoma growth driven by the Her2/neu pathway may be associated with tamoxifen chemoprevention failure in the rat mammary carcinoma model. Additionally, strategies combining targeted Her2/neu antibodies, vaccines or drugs with estrogen pathway modification may be more effective in reducing breast cancer chemoprevention failures.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Estrous cycle and ovarian changes in a rat mammary carcinogenesis model after irradiation, tamoxifen chemoprevention, and aging.Comp Med. 2003 Oct;53(5):532-8. Comp Med. 2003. PMID: 14655997
-
Neu-induced retroviral rat mammary carcinogenesis: a novel chemoprevention model for both hormonally responsive and nonresponsive mammary carcinomas.Cancer Res. 2006 Jul 1;66(13):6884-91. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1823. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16818667
-
Alcohol promotes mammary tumor development via the estrogen pathway in estrogen receptor alpha-negative HER2/neu mice.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012 Apr;36(4):577-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01654.x. Epub 2011 Oct 7. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012. PMID: 21981381
-
Inhibition of erbB receptor (HER) tyrosine kinases as a strategy to abrogate antiestrogen resistance in human breast cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2001 Dec;7(12 Suppl):4436s-4442s; discussion 4411s-4412s. Clin Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11916237 Review.
-
Chemosuppression of breast cancer with long-term tamoxifen therapy.Prev Med. 1991 Jan;20(1):3-14. doi: 10.1016/0091-7435(91)90002-l. Prev Med. 1991. PMID: 2008427 Review.
Cited by
-
A Randomized Phase IIb Study of Low-dose Tamoxifen in Chest-irradiated Cancer Survivors at Risk for Breast Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Feb 15;27(4):967-974. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-3609. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33272980 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Rat Models of Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2024 Jun 24;29(1):12. doi: 10.1007/s10911-024-09566-0. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2024. PMID: 38913216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adverse outcome pathways for ionizing radiation and breast cancer involve direct and indirect DNA damage, oxidative stress, inflammation, genomic instability, and interaction with hormonal regulation of the breast.Arch Toxicol. 2020 May;94(5):1511-1549. doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02752-z. Epub 2020 May 13. Arch Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32399610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pasireotide, an IGF-I action inhibitor, prevents growth hormone and estradiol-induced mammary hyperplasia.Pituitary. 2011 Mar;14(1):44-52. doi: 10.1007/s11102-010-0257-0. Pituitary. 2011. PMID: 20890664
-
Development of an adverse outcome pathway network for breast cancer: a comprehensive representation of the pathogenesis, complexity and diversity of the disease.Arch Toxicol. 2022 Nov;96(11):2881-2897. doi: 10.1007/s00204-022-03351-w. Epub 2022 Aug 4. Arch Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35927586 Review.
References
-
- Bhatia S, Robison LL, Oberlin O, Greenberg M, Bunin G, Fossati-Bellani F, Meadows AT. Breast cancer and other second neoplasms after childhood Hodgkin’s disease. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:745–51. - PubMed
-
- Bhatia S, Yasui Y, Robison LL, Birch JM, Bogue MK, Diller L, DeLaat C, Fossati-Bellani F, Morgan E, Oberlin O, Reaman G, Ruymann FB, Tersak J, Meadows AT. High risk of subsequent neoplasms continues with extended follow-up of childhood Hodgkin’s disease: report from the Late Effects Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:4386–94. - PubMed
-
- van Leeuwen FE, Klokman WJ, Stovall M, Dahler EC, van’t Veer MB, Noordijk EM, Crommelin MA, Aleman BM, Broeks A, Gospodarowicz M, Travis LB, Russell NS. Roles of radiation dose, chemotherapy, and hormonal factors in breast cancer following Hodgkin’s disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95:971–80. - PubMed
-
- Peto, R. (2000) Adjuvant hormone therapy: tamoxifen. NIH Consensus Development Conference: Adjuvant Therapy for Breast Cancer, Bethesda, Maryland.
-
- Tamoxifen for early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised trials. Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Lancet. 1998;351:1451–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

