Tumour necrosis factor receptor gene therapy affects cellular immune responses in collagen induced arthritis in mice
- PMID: 15860512
- PMCID: PMC1755256
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2004.025619
Tumour necrosis factor receptor gene therapy affects cellular immune responses in collagen induced arthritis in mice
Abstract
Background: Collagen induced arthritis (CIA) is an animal model of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) amenable to immunotherapy directed against tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha).
Objective: To evaluate whether local TNF receptor (TNF-R) gene therapy in DBA/1 mice exerts an influence beyond anti-inflammatory effects. Two measures of CIA pathogenesis were investigated-namely, immunity to collagen II (CII) 245-270 peptide (the major immunodominant epitope within bovine CII) and the preferential activation of T cell Vbeta8.2 variable region receptors in arthritic DBA/1 mice.
Methods: DBA/1 mice received single periarticular injections of media or retroviral vectors containing LacZ or human TNF-R into affected arthritic paws at disease onset. Disease severity was monitored, immune responses towards the immunodominant bovine CII 245-270 and subdominant CII 334-360 peptide epitopes were assessed by ELISA, and T cell Vbeta usage was analysed by real time polymerase chain reaction for the LacZ transduced, TNF-R, and viral-free media treated control animals. The therapeutic influence of TNF-R gene transduction was compared with other groups at different times after treatment.
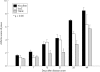
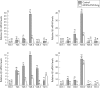
Results: Reduced disease severity was seen 15-35 days after treatment, with a concomitant increase in immunity towards the subdominant CII 334-360 peptide epitope rather than the immunodominant CII 245-270 peptide in TNF-R treated animals. Early in the disease, TNF-R treated animals demonstrated a reduction of bias towards the otherwise predominant Vbeta8.2 T cell subset.
Conclusions: TNF-R gene therapy influences cellular immunity in CIA, leading to overall disease amelioration, thus suggesting that TNF inhibition may have therapeutic potential beyond the control of inflammation in RA.
Figures
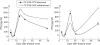

Similar articles
-
TNF receptor gene therapy results in suppression of IgG2a anticollagen antibody in collagen induced arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Aug;62(8):707-14. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.8.707. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003. PMID: 12860724 Free PMC article.
-
T cell immunity to type II collagen in the biobreeding rat: the identification and characterization of RT1u-restricted T cell epitopes on alpha 1(II).J Immunol. 2004 Aug 1;173(3):1795-801. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.3.1795. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15265910
-
IFNgamma deficient C57BL/6 (H-2b) mice develop collagen induced arthritis with predominant usage of T cell receptor Vbeta6 and Vbeta8 in arthritic joints.Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Oct;62(10):983-90. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.10.983. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003. PMID: 12972478 Free PMC article.
-
Oral administration of type-II collagen peptide 250-270 suppresses specific cellular and humoral immune response in collagen-induced arthritis.Clin Immunol. 2007 Jan;122(1):75-84. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2006.08.004. Epub 2006 Oct 11. Clin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17045846
-
Role of glycopeptide-specific T cells in collagen-induced arthritis: an example how post-translational modification of proteins may be involved in autoimmune disease.Ann Med. 2001 Oct;33(7):456-65. doi: 10.3109/07853890109002094. Ann Med. 2001. PMID: 11680793 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Liver x receptor agonist treatment on signal transduction pathways in acute lung inflammation.Respir Res. 2010 Feb 22;11(1):19. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-11-19. Respir Res. 2010. PMID: 20175894 Free PMC article.
-
Artesunate influences Th17/Treg lymphocyte balance by modulating Treg apoptosis and Th17 proliferation in a murine model of rheumatoid arthritis.Exp Ther Med. 2017 May;13(5):2267-2273. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4232. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28565837 Free PMC article.
-
A crucial role for tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 in synovial lining cells and the reticuloendothelial system in mediating experimental arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(2):R61. doi: 10.1186/ar2974. Epub 2010 Apr 6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20370892 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta attenuates the development of carrageenan-induced lung injury in mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Nov;149(6):687-702. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706902. Epub 2006 Oct 3. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17016509 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of PPAR-β/δ Attenuates Brain Injury by Suppressing Inflammation and Apoptosis in a Collagenase-Induced Intracerebral Hemorrhage Mouse Model.Neurochem Res. 2020 Apr;45(4):837-850. doi: 10.1007/s11064-020-02956-w. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Neurochem Res. 2020. PMID: 31939088 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

