Nurselike cells express BAFF and APRIL, which can promote survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells via a paracrine pathway distinct from that of SDF-1alpha
- PMID: 15860672
- PMCID: PMC1895149
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2004-03-0889
Nurselike cells express BAFF and APRIL, which can promote survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells via a paracrine pathway distinct from that of SDF-1alpha
Abstract
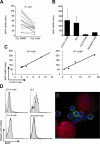
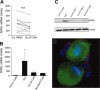
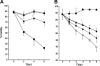
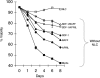
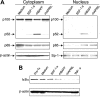
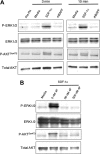
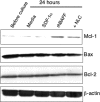
We examined expression of B cell-activating factor of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family (BAFF) and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL) on chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) B cells and nurselike cells (NLCs), which differentiate from CD14+ cells when cultured with CLL B cells. NLCs expressed significantly higher levels of APRIL than monocytes and significantly higher levels of BAFF and APRIL than CLL B cells. Also, the viability of CLL B cells cultured with NLCs was significantly reduced when CLL B cells were cultured with decoy receptor of B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA), which can bind both BAFF and APRIL, but not with BAFF receptor:Fc (BAFF-R:Fc), which binds only to BAFF. The effect(s) of BAFF or APRIL on leukemia cell survival appeared additive and distinct from that of stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha (SDF-1alpha), which in contrast to BAFF or APRIL induced leukemia cell phosphorylation of p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase (extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 [ERK1/2]) and AKT. Conversely, BAFF and APRIL, but not SDF-1alpha, induced CLL-cell activation of the nuclear factor-kappaB1 (NF-kappaB1) and enhanced CLL-cell expression of the antiapoptotic protein Mcl-1. However, BAFF, but not APRIL, also induced CLL-cell activation of NF-kappaB2. We conclude that BAFF and APRIL from NLCs can function in a paracrine manner to support leukemia cell survival via mechanisms that are distinct from those of SDF-1alpha, indicating that NLCs use multiple distinct pathways to support CLL-cell survival.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Involvement of BAFF and APRIL in the resistance to apoptosis of B-CLL through an autocrine pathway.Blood. 2004 Jan 15;103(2):679-88. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-02-0540. Epub 2003 Sep 22. Blood. 2004. PMID: 14504101
-
Lymphoma B cells evade apoptosis through the TNF family members BAFF/BLyS and APRIL.J Immunol. 2004 Mar 1;172(5):3268-79. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.5.3268. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14978135
-
BAFF and APRIL support chronic lymphocytic leukemia B-cell survival through activation of the canonical NF-kappaB pathway.Blood. 2007 Jan 15;109(2):703-10. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-06-027755. Epub 2006 Sep 14. Blood. 2007. PMID: 16973958 Free PMC article.
-
Role of BAFF and APRIL in human B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.Immunology. 2006 Jul;118(3):281-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2006.02377.x. Immunology. 2006. PMID: 16827889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BAFF and the regulation of B cell survival.Immunol Lett. 2003 Jul 3;88(1):57-62. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2478(03)00050-6. Immunol Lett. 2003. PMID: 12853163 Review.
Cited by
-
Stromal endothelial cells establish a bidirectional crosstalk with chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells through the TNF-related factors BAFF, APRIL, and CD40L.J Immunol. 2012 Jun 15;188(12):6071-83. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102066. Epub 2012 May 16. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22593611 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic value of serum levels of a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL) in treatment-naïve patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Turk J Med Sci. 2021 Feb 26;51(1):348-354. doi: 10.3906/sag-2004-282. Turk J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 32950049 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma B-Cell Maturation Antigen Levels are Elevated and Correlate with Disease Activity in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.Target Oncol. 2019 Oct;14(5):551-561. doi: 10.1007/s11523-019-00666-0. Target Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31473933
-
Molecular Interactions Between Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Their Therapeutic Implications.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 26;9:2720. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02720. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30542344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells receive RAF-dependent survival signals in response to CXCL12 that are sensitive to inhibition by sorafenib.Blood. 2011 Jan 20;117(3):882-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-04-282400. Epub 2010 Nov 15. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21079155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kipps TJ. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia and related diseases. In: Beutler E, Lichtman MA, Coller BS, Kipps TJ, Seligsohn U, eds. Williams Hematology. 6th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2001: 1163-1194.
-
- McConkey DJ, Chandra J, Wright S, et al. Apoptosis sensitivity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is determined by endogenous endonuclease content and relative expression of BCL-2 and BAX. J Immunol. 1996;156: 2624-2630. - PubMed
-
- Kitada S, Andersen J, Akar S, et al. Expression of apoptosis-regulating proteins in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: correlations with in vitro and in vivo chemoresponses. Blood. 1998;91: 3379-3389. - PubMed
-
- Collins RJ, Verschuer LA, Harmon BV, Prentice RL, Pope JH, Kerr JF. Spontaneous programmed death (apoptosis) of B-chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells following their culture in vitro. Br J Haematol. 1989;71: 343-350. - PubMed
-
- Holder MJ, Wang H, Milner AE, et al. Suppression of apoptosis in normal and neoplastic human B lymphocytes by CD40 ligand is independent of Bc1–2 induction. Eur J Immunol. 1993;23: 2368-2371. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

