Multiplex amplification enabled by selective circularization of large sets of genomic DNA fragments
- PMID: 15860768
- PMCID: PMC1087789
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gni070
Multiplex amplification enabled by selective circularization of large sets of genomic DNA fragments
Abstract
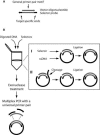
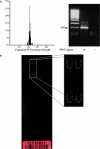
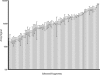
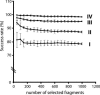
We present a method to specifically select large sets of DNA sequences for parallel amplification by PCR using target-specific oligonucleotide constructs, so-called selectors. The selectors are oligonucleotide duplexes with single-stranded target-complementary end-sequences that are linked by a general sequence motif. In the selection process, a pool of selectors is combined with denatured restriction digested DNA. Each selector hybridizes to its respective target, forming individual circular complexes that are covalently closed by enzymatic ligation. Non-circularized fragments are removed by exonucleolysis, enriching for the selected fragments. The general sequence that is introduced into the circularized fragments allows them to be amplified in parallel using a universal primer pair. The procedure avoids amplification artifacts associated with conventional multiplex PCR where two primers are used for each target, thereby reducing the number of amplification reactions needed for investigating large sets of DNA sequences. We demonstrate the specificity, reproducibility and flexibility of this process by performing a 96-plex amplification of an arbitrary set of specific DNA sequences, followed by hybridization to a cDNA microarray. Eighty-nine percent of the selectors generated PCR products that hybridized to the expected positions on the array, while little or no amplification artifacts were observed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PieceMaker: selection of DNA fragments for selector-guided multiplex amplification.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Apr 28;33(8):e72. doi: 10.1093/nar/gni071. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15860769 Free PMC article.
-
DNA analysis with multiplex microarray-enhanced PCR.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jan 20;33(2):e11. doi: 10.1093/nar/gnh184. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15661850 Free PMC article.
-
Amplification of circularizable probes for the detection of target nucleic acids and proteins.Clin Chim Acta. 2006 Jan;363(1-2):61-70. doi: 10.1016/j.cccn.2005.05.039. Epub 2005 Aug 24. Clin Chim Acta. 2006. PMID: 16122721 Review.
-
[A method of selective PCR-amplification of genomic DNA fragments (SAGF method)].Biokhimiia. 1995 Sep;60(9):1363-70. Biokhimiia. 1995. PMID: 8562645 Russian.
-
The real-time polymerase chain reaction.Mol Aspects Med. 2006 Apr-Jun;27(2-3):95-125. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2005.12.007. Epub 2006 Feb 3. Mol Aspects Med. 2006. PMID: 16460794 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery and application of insertion-deletion (INDEL) polymorphisms for QTL mapping of early life-history traits in Atlantic salmon.BMC Genomics. 2010 Mar 8;11:156. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-156. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20210987 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Ecology: Where are we now?Postdoc J. 2016 Nov;4(11):3-17. doi: 10.14304/SURYA.JPR.V4N11.2. Postdoc J. 2016. PMID: 27975077 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and highly-specific generation of targeted DNA sequencing libraries enabled by linking capture probes with universal primers.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 5;13(12):e0208283. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208283. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30517195 Free PMC article.
-
PieceMaker: selection of DNA fragments for selector-guided multiplex amplification.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Apr 28;33(8):e72. doi: 10.1093/nar/gni071. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15860769 Free PMC article.
-
Low-abundance mutations in colorectal cancer patients and healthy adults.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Jan 12;12(1):808-824. doi: 10.18632/aging.102657. Epub 2020 Jan 12. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 31927530 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saiki R.K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K.B., Horn G.T., Erlich H.A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985;230:1350–1354. - PubMed
-
- Telenius H., Carter N.P., Bebb C.E., Nordenskjold M., Ponder B.A., Tunnacliffe A. Degenerate oligonucleotide-primed PCR: general amplification of target DNA by a single degenerate primer. Genomics. 1992;13:718–725. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

