Suppression of vascular endothelial growth factor expression at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels
- PMID: 15860771
- PMCID: PMC1087787
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gni068
Suppression of vascular endothelial growth factor expression at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels
Abstract
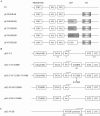
Gene expression is regulated at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. Therefore, in order to achieve a high level of silencing, which includes minimizing any residual expression of a target gene, suppression at both the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels is required. In this study, we describe a new method for highly efficient gene silencing that combines zinc finger protein-mediated transcriptional repression and small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated inhibition of post-transcriptional events. To measure the amount of gene expression under various conditions, we used a luciferase reporter gene that was driven by a variety of promoters, including that of the human vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) gene. We also measured expression of the endogenous VEGF-A gene. Inhibition of gene expression by each of the two individual technologies was effective, but in-depth analyses revealed residual expression of the target gene. The combination of specific zinc finger transcription factors and siRNAs greatly enhanced the silencing of the human VEGF-A gene, not only when cells were grown in the presence of normal amounts of oxygen but also under conditions of hypoxic stimulation. These results suggest that a bi-level approach to the silencing of VEGF-A expression may be clinically beneficial as part of a cancer treatment protocol.
Figures
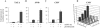
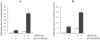
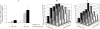
Similar articles
-
Intended transcriptional silencing with siRNA results in gene repression through sequence-specific off-targeting.RNA. 2010 Feb;16(2):430-41. doi: 10.1261/rna.1808510. Epub 2009 Dec 21. RNA. 2010. PMID: 20026621 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of hypoxia-related gene expression in sarcomas and effect of hypoxia on RNA interference of vascular endothelial cell growth factor A.Cancer Res. 2005 Jul 1;65(13):5881-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4078. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15994966
-
Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor gene under hypoxia by using artificial transcription factors.Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (Oxf). 2009;(53):289-90. doi: 10.1093/nass/nrp145. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (Oxf). 2009. PMID: 19749374
-
Repression of vascular endothelial growth factor expression by the zinc finger transcription factor ZNF24.Cancer Res. 2007 Sep 15;67(18):8736-41. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1617. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17875714
-
Endothelial PAS domain protein 1 gene promotes angiogenesis through the transactivation of both vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor, Flt-1.Circ Res. 2004 Jul 23;95(2):146-53. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000134920.10128.b4. Epub 2004 Jun 10. Circ Res. 2004. PMID: 15192019
Cited by
-
Modular assembly of designer PUF proteins for specific post-transcriptional regulation of endogenous RNA.J Biol Eng. 2014 Mar 1;8(1):7. doi: 10.1186/1754-1611-8-7. J Biol Eng. 2014. PMID: 24581042 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-specific downregulation of endogenous human VEGF-A gene by hypoxia-driven expression of artificial transcription factor.Mol Biotechnol. 2010 Oct;46(2):134-9. doi: 10.1007/s12033-010-9288-z. Mol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20473588
-
Two-dimensional differential in-gel electrophoresis proteomic approaches reveal urine candidate biomarkers in pediatric obstructive sleep apnea.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009 Dec 15;180(12):1253-61. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200905-0765OC. Epub 2009 Sep 24. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009. PMID: 19797158 Free PMC article.
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor: implications for tumor angiogenesis.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Aug 21;12(31):4937-42. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i31.4937. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16937487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted genome editing in human cells with zinc finger nucleases constructed via modular assembly.Genome Res. 2009 Jul;19(7):1279-88. doi: 10.1101/gr.089417.108. Epub 2009 May 21. Genome Res. 2009. PMID: 19470664 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fire A., Xu S., Montgomery M.K., Kostas S.A., Driver S.E., Mello C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
-
- Hammond S.M., Boettcher S., Caudy A.A., Kobayashi R., Hannon G.J. Argonaute2, a link between genetic and biochemical analyses of RNAi. Science. 2001;293:1146–1150. - PubMed
-
- Gonczy P., Echeverri C., Oegema K., Coulson A., Jones S.J., Copley R.R., Duperon J., Oegema J., Brehm M., Cassin E., et al. Functional genomic analysis of cell division in C. elegans using RNAi of genes on chromosome III. Nature. 2000;408:331–336. - PubMed
-
- Kennerdell J.R., Carthew R.W. Heritable gene silencing in Drosophila using double-stranded RNA. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000;18:896–898. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

