APF, HB-EGF, and EGF biomarkers in patients with ulcerative vs. non-ulcerative interstitial cystitis
- PMID: 15862132
- PMCID: PMC1131910
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2490-5-7
APF, HB-EGF, and EGF biomarkers in patients with ulcerative vs. non-ulcerative interstitial cystitis
Abstract
Background: Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder disorder, with symptoms including pelvic and or perineal pain, urinary frequency, and urgency. The etiology of IC is unknown, but sensitive and specific biomarkers have been described, including antiproliferative factor (APF), heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor (HB-EGF), and epidermal growth factor (EGF). However, the relative sensitivity of these biomarkers in ulcerative vs. nonulcerative IC is unknown, and these markers have yet to be validated in another laboratory. We therefore measured these markers in urine from patients with or without Hunner's ulcer, as well as normal controls, patients with bladder cancer, and patients with bacterial cystitis, at the First Hospital of China Medical University.
Methods: Urine specimens were collected from two groups of Chinese IC patients (38 IC patients with Hunner's ulcers, 26 IC patients without Hunner's ulcers), 30 normal controls, 10 bacterial cystitis patients and 10 bladder cancer patients. APF activity was determined by measuring 3H-thymidine incorporation in vitro, and HB-EGF and EGF levels were determined by ELISA.
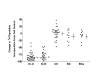
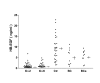
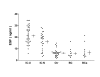
Results: APF activity (inhibition of thymidine incorporation) was significantly greater in all IC patient urine specimens than in normal control specimens or in specimens from patients with bacterial cystitis or bladder cancer (p < 0.0001 for each comparison). Urine HB-EGF levels were also significantly lower and EGF levels significantly higher in both groups of IC patients than in the three control groups (p < 0.0001 for each comparison). Although APF and HB-EGF levels were similar in ulcerative and nonulcerative IC patients, EGF levels were significantly higher in IC patients with vs. without ulcers (p < 0.004).
Conclusion: These findings indicate that APF, HB-EGF and EGF are good biomarkers for both ulcerative and nonulcerative IC and validate their measurement as biomarkers for IC in Chinese patients.
Figures
References
-
- Hanno PM, Staskin DR, Krane RJ, Wein AJ, eds . Interstitial cystitis. Springer-Verlag, London; 1990.
-
- Division of Kidney, Urologic, and Hematologic Diseases (DKUHD) of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) Diagnostic criteria for research studies (interstitial cystitis) Am J Kidney Dis. 1989;13:353–354.
-
- Zhang C-O, Li Z-L, Shoenfelt JL, Kong C-Z, Chai TC, Erickson DE, Peters KM, Rovner ES, Keay S. Comparison of APF activity and epithelial growth factor levels in urine from Chinese, African American and Caucasian American IC patients. Urology. 2003;61:897–901. doi: 10.1016/S0090-4295(02)02597-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Keay S, Zhang C-O, Shoenfelt JL, Erickson DR, Whitmore K, Warren JW, Marvel R, Chai T. Sensitivity and specificity of antiproliferative factor, heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor, and epidermal growth factor as urine markers for interstitial cystitis. Urology. 2001;57:9–14. doi: 10.1016/S0090-4295(01)01127-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

