Precise and parallel characterization of coding polymorphisms, alternative splicing, and modifications in human proteins by mass spectrometry
- PMID: 15863400
- PMCID: PMC1307493
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M500064-MCP200
Precise and parallel characterization of coding polymorphisms, alternative splicing, and modifications in human proteins by mass spectrometry
Abstract
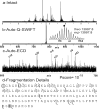
The human proteome is a highly complex extension of the genome wherein a single gene often produces distinct protein forms due to alternative splicing, RNA editing, polymorphisms, and posttranslational modifications. Such biological variation compounded by the high sequence identity within gene families currently overwhelms the complete and routine characterization of mammalian proteins by MS. A new data base of human proteins (and their possible variants) was created and searched using tandem mass spectrometric data from intact proteins. This first application of top down MS/MS to wild-type human proteins demonstrates both gene-specific identification and the unambiguous characterization of multifaceted mass shifts (Deltam values). Such Deltam values found from the precise identification of 45 protein forms from HeLa cells reveal 34 coding single nucleotide polymorphisms, two protein forms from alternative splicing, and 12 diverse modifications (not including simple N-terminal processing), including a previously unknown phosphorylation at 10% occupancy. Automated protein identification was achieved with a median expectation value of 10(-13) and often occurred simultaneously with dissection of diverse sources of protein variability as they occur in combination. Top down MS therefore has a bright future for enabling precise annotation of gene products expressed from the human genome by non-mass spectrometrists.
Figures



References
-
- Aebersold R, Mann M. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature. 2003;422:198–207. - PubMed
-
- Yates JR. Mass spectral analysis in proteomics. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2004;33:297–316. - PubMed
-
- Hines WM, Parker K, Peltier J, Patterson DH, Vestal ML, Martin SA. Protein identification and protein characterization by high-performance time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Protein Chem. 1998;17:525–526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

