Replacement of K-Ras with H-Ras supports normal embryonic development despite inducing cardiovascular pathology in adult mice
- PMID: 15864294
- PMCID: PMC1299307
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400397
Replacement of K-Ras with H-Ras supports normal embryonic development despite inducing cardiovascular pathology in adult mice
Abstract
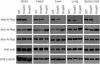
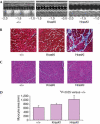
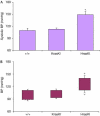
Ras proteins are highly related GTPases that have key roles in regulating growth, differentiation and tumorigenesis. Gene-targeting experiments have shown that, out of the three mammalian ras genes, only K-ras is essential for normal mouse embryogenesis, and that mice deprived of H-ras and/or N-ras show no major phenotype. We generated mice (HrasKI) in which the K-ras gene had been modified to encode H-Ras protein. HrasKI mice produce undetectable amounts of K-Ras but-in contrast to mice homozygous for a null K-ras allele-they are born at the expected mendelian frequency, indicating that H-Ras can be substituted for K-Ras in embryonic development. However, adult HrasKI mice show dilated cardiomyopathy associated with arterial hypertension. Our results show that K-Ras can be replaced by H-Ras in its essential function in embryogenesis, and indicate that K-Ras has a unique role in cardiovascular homeostasis.
Figures

References
-
- Bergo MO, Lieu HD, Gavino BJ, Ambroziak P, Otto JC, Casey PJ, Walker QM, Young SG (2004) On the physiological importance of endoproteolysis of CAAX proteins: heartspecific RCE1 knockout mice develop a lethal cardiomyopathy. J Biol Chem 279: 4729–4736 - PubMed
-
- Brancaccio M et al. (2003) Melusin, a musclespecific integrin β1-interacting protein, is required to prevent cardiac failure in response to chronic pressure overload. Nat Med 9: 68–75 - PubMed
-
- Chen KH et al. (2004) Dysregulation of HSG triggers vascular proliferative disorders. Nat Cell Biol 6: 872–883 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

