Endocannabinoid signaling depends on the spatial pattern of synapse activation
- PMID: 15864304
- PMCID: PMC2629534
- DOI: 10.1038/nn1458
Endocannabinoid signaling depends on the spatial pattern of synapse activation
Abstract
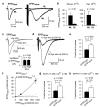
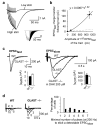
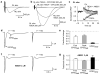
The brain's endocannabinoid retrograde messenger system decreases presynaptic transmitter release, but its physiological function is uncertain. We show that endocannabinoid signaling is absent when spatially dispersed synapses are activated on rodent cerebellar Purkinje cells but that it reduces presynaptic glutamate release when nearby synapses are active. This switching of signaling according to the spatial pattern of activity is controlled by postsynaptic type I metabotropic glutamate receptors, which are activated disproportionately when glutamate spillover between synapses produces synaptic crosstalk. When spatially distributed synapses are activated, endocannabinoid inhibition of transmitter release can be rescued by inhibiting glutamate uptake to increase glutamate spillover. Endocannabinoid signaling initiated by type I metabotropic glutamate receptors is a homeostatic mechanism that detects synaptic crosstalk and downregulates glutamate release in order to promote synaptic independence.
Figures

References
-
- Wilson RI, Nicoll RA. Endocannabinoid signalling in the brain. Science. 2002;296:678–682. - PubMed
-
- Kreitzer AC, Regehr WG. Retrograde signaling by endocannabinoids. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2002;12:324–330. - PubMed
-
- Ito M. Cerebellar long-term depression: characterization, signal transduction, and functional roles. Physiol. Rev. 2001;81:1143–1195. - PubMed
-
- Barbour B, Hausser M. Intersynaptic diffusion of transmitter. Trends Neurosci. 1997;20:377–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

