Food for thought: endocannabinoid modulation of lipogenesis
- PMID: 15864340
- PMCID: PMC1087183
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI25076
Food for thought: endocannabinoid modulation of lipogenesis
Abstract
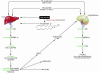
An emerging body of evidence implicates peripheral and central endocannabinoid pathways in the regulation of feeding behavior and body weight. A report in this issue of the JCI demonstrates the presence of a common endocannabinoid-regulated molecular pathway for peripheral lipogenic and central appetitive regulation. This pathway involves the activation of the transcription factor SREBP-1c and its associated enzymes, acetyl-CoA carboxylase-1 and fatty acid synthase, in the liver and hypothalamus. Activation of cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB(1)) in liver plays a key role in increased serum lipid production, fatty liver, and possibly diet-induced obesity. Conversely, stimulation of these receptors in the hypothalamus may lead to an increase in food consumption. Thus, targeting both of these pathways with CB(1) antagonists could promote sustained weight loss and favorable serum lipid profiles in obese patients.
Figures
Comment on
-
Endocannabinoid activation at hepatic CB1 receptors stimulates fatty acid synthesis and contributes to diet-induced obesity.J Clin Invest. 2005 May;115(5):1298-305. doi: 10.1172/JCI23057. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 15864349 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abel, E.L. 1980. Marijuana: the first twelve thousand years. Plemum Press. New York, New York, USA. 289 pp.
-
- Gaoni Y, Mechoulam R. Isolation, structure, and partial synthesis of an active constituent of hashish. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964;86:1646–1647.
-
- Berry EM, Mechoulam R. Tetrahydrocannabinol and endocannabinoids in feeding and appetite. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002;95:185–190. - PubMed
-
- Beal JA, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of dronabinol for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated anorexia. J. Pain Symptom Manage. 1997;14:7–14. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda LA, Bonner TI, Lolait SJ. Localization of cannabinoid receptor mRNA in rat brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 1993;327:535–550. - PubMed

