Virus-induced dysfunction of CD4+CD25+ T cells in patients with HTLV-I-associated neuroimmunological disease
- PMID: 15864353
- PMCID: PMC1087174
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI23913
Virus-induced dysfunction of CD4+CD25+ T cells in patients with HTLV-I-associated neuroimmunological disease
Abstract
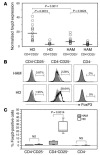
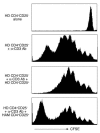
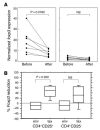
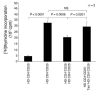
CD4(+)CD25(+) Tregs are important in the maintenance of immunological self tolerance and in the prevention of autoimmune diseases. As the CD4(+)CD25(+) T cell population in patients with human T cell lymphotropic virus type I-associated (HTLV-I-associated) myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) has been shown to be a major reservoir for this virus, it was of interest to determine whether the frequency and function of CD4(+)CD25(+) Tregs in HAM/TSP patients might be affected. In these cells, both mRNA and protein expression of the forkhead transcription factor Foxp3, a specific marker of Tregs, were lower than those in CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells from healthy individuals. The virus-encoded transactivating HTLV-I tax gene was demonstrated to have a direct inhibitory effect on Foxp3 expression and function of CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells. This is the first report to our knowledge demonstrating the role of a specific viral gene product (HTLV-I Tax) on the expression of genes associated with Tregs (in particular, foxp3) resulting in inhibition of Treg function. These results suggest that direct human retroviral infection of CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells may be associated with the pathogenesis of HTLV-I-associated neurologic disease.
Figures
Comment in
-
A tax on luxury: HTLV-I infection of CD4+CD25+ Tregs.J Clin Invest. 2005 May;115(5):1144-6. doi: 10.1172/JCI25130. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 15864345 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Osame M, et al. HTLV-I associated myelopathy, a new clinical entity [letter] Lancet. 1986;1:1031–1032. - PubMed
-
- Gessain A, et al. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-I in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet. 1985;2:407–410. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan JE, et al. The risk of development of HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis among persons infected with HTLV-I. J. Acquir. Immune. Defic. Syndr. 1990;3:1096–1101. - PubMed
-
- Nakagawa M, et al. HTLV-I-associated myelopathy: analysis of 213 patients based on clinical features and laboratory findings. J. Neurovirol. 1995;1:50–61. - PubMed
-
- Uchiyama T. Human T cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) and human diseases. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1997;15:15–37. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

