Mechanistic studies of mouse polyamine oxidase with N1,N12-bisethylspermine as a substrate
- PMID: 15865452
- PMCID: PMC1635011
- DOI: 10.1021/bi050347k
Mechanistic studies of mouse polyamine oxidase with N1,N12-bisethylspermine as a substrate
Abstract
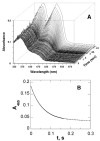
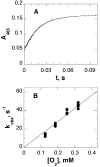
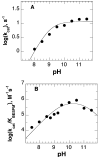
In mammalian cells, the flavoprotein polyamine oxidase catalyzes a key step in the catabolism of polyamines, the oxidation of N1-acetylspermine and N1-acetylspermidine to spermidine and putrescine, respectively. The mechanism of the mouse enzyme has been studied with N1,N12-bisethylspermine (BESPM) as a substrate. At pH 10, the pH optimum, the limiting rate of reduction of the flavin in the absence of oxygen is comparable to the k(cat) value for turnover, establishing reduction as rate-limiting. Oxidation of the reduced enzyme is a simple second-order reaction. No intermediates are seen in the reductive or oxidative half-reactions. The k(cat) value decreases below a pK(a) of 9.0. The k(cat)/K(m) value for BESPM exhibits a bell-shaped pH profile, with pK(a) values of 9.8 and 10.8. These pK(a) values are assigned to the substrate nitrogens. The rate constant for the reaction of the reduced enzyme with oxygen is not affected by a pH between 7.5 and 10. Active site residue Tyr430 is conserved in the homologous protein monoamine oxidase. Mutation of this residue to phenylalanine results in a 6-fold decrease in the k(cat) value and the k(cat)/K(m) value for oxygen due to a comparable decrease in the rate constant for flavin reduction. This moderate change is not consistent with this residue forming a tyrosyl radical during catalysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanistic studies of human spermine oxidase: kinetic mechanism and pH effects.Biochemistry. 2010 Jan 19;49(2):386-92. doi: 10.1021/bi9017945. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20000632 Free PMC article.
-
pH dependence of a mammalian polyamine oxidase: insights into substrate specificity and the role of lysine 315.Biochemistry. 2009 Feb 24;48(7):1508-16. doi: 10.1021/bi802227m. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19199575 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic studies of the yeast polyamine oxidase Fms1: kinetic mechanism, substrate specificity, and pH dependence.Biochemistry. 2010 Dec 14;49(49):10440-8. doi: 10.1021/bi1016099. Epub 2010 Nov 16. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 21067138 Free PMC article.
-
Interconversion, catabolism and elimination of the polyamines.Med Biol. 1981 Dec;59(5-6):334-46. Med Biol. 1981. PMID: 7040832 Review.
-
Catabolism of polyamines.Amino Acids. 2004 Jun;26(3):217-33. doi: 10.1007/s00726-004-0070-z. Epub 2004 Apr 20. Amino Acids. 2004. PMID: 15221502 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic studies of the role of a conserved histidine in a mammalian polyamine oxidase.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012 Dec 1;528(1):45-9. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2012.08.007. Epub 2012 Aug 30. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012. PMID: 22959971 Free PMC article.
-
Structures and Mechanism of the Monoamine Oxidase Family.Biomol Concepts. 2011 Oct 1;2(5):365-377. doi: 10.1515/BMC.2011.030. Biomol Concepts. 2011. PMID: 22022344 Free PMC article.
-
13C kinetic isotope effects on the reaction of a flavin amine oxidase determined from whole molecule isotope effects.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016 Dec 15;612:115-119. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2016.10.018. Epub 2016 Nov 1. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016. PMID: 27815088 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidation of amines by flavoproteins.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010 Jan 1;493(1):13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2009.07.019. Epub 2009 Aug 3. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010. PMID: 19651103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic studies of human spermine oxidase: kinetic mechanism and pH effects.Biochemistry. 2010 Jan 19;49(2):386-92. doi: 10.1021/bi9017945. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20000632 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tabor CW, Tabor H. Polyamines. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1984;53:749–790. - PubMed
-
- Marton LJ, Pegg AE. Polyamines as targets for therapeutic intervention. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1995;35:55–91. - PubMed
-
- Bergeron RJ, Feng Y, Weimar WR, McManis JS, Dimova H, Porter C, Raisler B, Phanstiel O. A comparison of structure–activity relationships between spermidine and spermine analogue antineoplastics. J. Med. Chem. 1997;40:1475–1494. - PubMed
-
- Bitonti AJ, Dumont JA, Bush TL, Stemerick DM, Edwards ML. Bis(benzyl)polyamine analogs as novel substrates for polyamine oxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 1990;265:382–388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

