Coatomer-bound Cdc42 regulates dynein recruitment to COPI vesicles
- PMID: 15866890
- PMCID: PMC2171931
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200501157
Coatomer-bound Cdc42 regulates dynein recruitment to COPI vesicles
Abstract
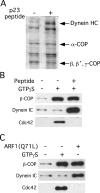
Cytoskeletal dynamics at the Golgi apparatus are regulated in part through a binding interaction between the Golgi-vesicle coat protein, coatomer, and the regulatory GTP-binding protein Cdc42 (Wu, W.J., J.W. Erickson, R. Lin, and R.A. Cerione. 2000. Nature. 405:800-804; Fucini, R.V., J.L. Chen, C. Sharma, M.M. Kessels, and M. Stamnes. 2002. Mol. Biol. Cell. 13:621-631). The precise role of this complex has not been determined. We have analyzed the protein composition of Golgi-derived coat protomer I (COPI)-coated vesicles after activating or inhibiting signaling through coatomer-bound Cdc42. We show that Cdc42 has profound effects on the recruitment of dynein to COPI vesicles. Cdc42, when bound to coatomer, inhibits dynein binding to COPI vesicles whereas preventing the coatomer-Cdc42 interaction stimulates dynein binding. Dynein recruitment was found to involve actin dynamics and dynactin. Reclustering of nocodazole-dispersed Golgi stacks and microtubule/dynein-dependent ER-to-Golgi transport are both sensitive to disrupting Cdc42 mediated signaling. By contrast, dynein-independent transport to the Golgi complex is insensitive to mutant Cdc42. We propose a model for how proper temporal regulation of motor-based vesicle translocation could be coupled to the completion of vesicle formation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cdc42 regulates microtubule-dependent Golgi positioning.Traffic. 2010 Aug;11(8):1067-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01082.x. Epub 2010 May 26. Traffic. 2010. PMID: 20525016 Free PMC article.
-
Cytosol-derived proteins are sufficient for Arp2/3 recruitment and ARF/coatomer-dependent actin polymerization on Golgi membranes.FEBS Lett. 2004 May 21;566(1-3):281-6. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.04.061. FEBS Lett. 2004. PMID: 15147909
-
Cdc42 and Cellular Polarity: Emerging Roles at the Golgi.Trends Cell Biol. 2016 Apr;26(4):241-248. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2015.11.003. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Trends Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26704441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bicaudal-D regulates COPI-independent Golgi-ER transport by recruiting the dynein-dynactin motor complex.Nat Cell Biol. 2002 Dec;4(12):986-92. doi: 10.1038/ncb891. Nat Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12447383
-
Formation of COPI-coated vesicles at a glance.J Cell Sci. 2018 Mar 13;131(5):jcs209890. doi: 10.1242/jcs.209890. J Cell Sci. 2018. PMID: 29535154 Review.
Cited by
-
The distinct localization of CDC42 isoforms is responsible for their specific functions during migration.J Cell Biol. 2024 Mar 4;223(3):e202004092. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202004092. Epub 2024 Feb 22. J Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38386112 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles for Rho GTPases operating at the Golgi complex.Small GTPases. 2021 Sep-Nov;12(5-6):311-322. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2020.1812873. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Small GTPases. 2021. PMID: 32881632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Copb1-facilitated axonal transport and translation of kappa opioid-receptor mRNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Aug 21;104(34):13810-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0703805104. Epub 2007 Aug 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17698811 Free PMC article.
-
Rho GTPases, phosphoinositides, and actin: a tripartite framework for efficient vesicular trafficking.Small GTPases. 2014;5:e29469. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.29469. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 24914539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights into how the Rho guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor regulates the interaction of Cdc42 with membranes.J Biol Chem. 2009 Aug 28;284(35):23860-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.031815. Epub 2009 Jul 6. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19581296 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

