Biofilm formation and sloughing in Serratia marcescens are controlled by quorum sensing and nutrient cues
- PMID: 15866935
- PMCID: PMC1111991
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.10.3477-3485.2005
Biofilm formation and sloughing in Serratia marcescens are controlled by quorum sensing and nutrient cues
Abstract
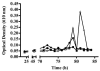
We describe here a role for quorum sensing in the detachment, or sloughing, of Serratia marcescens filamentous biofilms, and we show that nutrient conditions affect the biofilm morphotype. Under reduced carbon or nitrogen conditions, S. marcescens formed a classical biofilm consisting of microcolonies. The filamentous biofilm could be converted to a microcolony-type biofilm by switching the medium after establishment of the biofilm. Similarly, when initially grown as a microcolony biofilm, S. marcescens could be converted back to a filamentous biofilm by increasing the nutrient composition. Under high-nutrient conditions, an N-acyl homoserine lactone quorum-sensing mutant formed biofilms that were indistinguishable from the wild-type biofilms. Similarly, other quorum-sensing-dependent behaviors, such as swarming motility, could be rendered quorum sensing independent by manipulating the growth medium. Quorum sensing was also found to be involved in the sloughing of the filamentous biofilm. The biofilm formed by the bacterium consistently sloughed from the substratum after approximately 75 to 80 h of development. The quorum-sensing mutant, when supplemented with exogenous signal, formed a wild-type filamentous biofilm and sloughed at the same time as the wild type, and this was independent of surfactant production. When we removed the signal from the quorum-sensing mutant prior to the time of sloughing, the biofilm did not undergo significant detachment. Together, the data suggest that biofilm formation by S. marcescens is a dynamic process that is controlled by both nutrient cues and the quorum-sensing system.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of quorum sensing mediated developmental traits in the resistance of Serratia marcescens biofilms against protozoan grazing.Environ Microbiol. 2006 Jun;8(6):1017-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.00993.x. Environ Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16689722
-
The function of SpnR and the inhibitory effects by halogenated furanone on quorum sensing in Serratia marcescens AS-1.Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2008 Mar;48(3):391-7. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 18479069
-
Role of quorum sensing and antimicrobial component production by Serratia plymuthica in formation of biofilms, including mixed biofilms with Escherichia coli.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 Nov;72(11):7294-300. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01708-06. Epub 2006 Sep 22. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16997989 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum sensing in Serratia.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2007 Jul;31(4):407-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00071.x. Epub 2007 Apr 25. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17459113 Review.
-
Environmental signals and regulatory pathways that influence biofilm formation.Mol Microbiol. 2004 May;52(4):917-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04036.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15130114 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphate limitation induces the intergeneric inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Serratia marcescens isolated from paper machines.FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2013 Jun;84(3):577-87. doi: 10.1111/1574-6941.12086. Epub 2013 Mar 11. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2013. PMID: 23398522 Free PMC article.
-
Process-Oriented Review of Bacterial Quorum Quenching for Membrane Biofouling Mitigation in Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs).Membranes (Basel). 2016 Dec 13;6(4):52. doi: 10.3390/membranes6040052. Membranes (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27983578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biocompatibility and biofilm inhibition of N,N-hexyl,methyl-polyethylenimine bonded to Boston Keratoprosthesis materials.Biomaterials. 2011 Dec;32(34):8783-96. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.08.010. Epub 2011 Sep 7. Biomaterials. 2011. PMID: 21903257 Free PMC article.
-
Towards standardized mechanical characterization of microbial biofilms: analysis and critical review.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2018 Aug 20;4:17. doi: 10.1038/s41522-018-0062-5. eCollection 2018. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2018. PMID: 30131867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-acyl-L-homoserine lactone quorum sensing controls butanediol fermentation in Serratia plymuthica RVH1 and Serratia marcescens MG1.J Bacteriol. 2006 Jun;188(12):4570-2. doi: 10.1128/JB.00144-06. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16740963 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

