Blocking IL-1 in systemic inflammation
- PMID: 15867089
- PMCID: PMC2213199
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20050640
Blocking IL-1 in systemic inflammation
Abstract
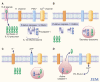
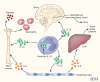
A growing number of systemic inflammatory diseases characterized in part by recurrent fevers, leukocytosis, anemia, and elevated acute phase proteins are linked to interleukin (IL)-1 activity since rapid and sustained resolution is observed upon specific blockade of IL-1 receptors. Rapid resolution of systemic and local inflammation is now also reported in systemic onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis (SoJIA). Loss of control of the secretion of IL-1beta might be a common mechanism explaining the aberrant activity of IL-1 in these diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Tschopp, J., F. Martinon, and K. Burns. 2003. NALPs: a novel protein family involved in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4:95–104. - PubMed
-
- Gudipaty, L., J. Munetz, P.A. Verhoef, and G.R. Dubyak. 2003. Essential role for Ca2+ in the regulation of IL-1β secretion by P2X7 nucleotide receptor in monocytes, macrophages, and HEK-293 cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 285:C286–C299. - PubMed
-
- Solle, M., J. Labasi, D.G. Perregaux, E. Stam, N. Petrushova, B.H. Koller, R.J. Griffiths, and C.A. Gabel. 2001. Altered cytokine production in mice lacking P2X(7) receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 276:125–132. - PubMed
-
- Elssner, A., M. Duncan, M. Gavrilin, and M.D. Wewers. 2004. A novel P2X7 receptor activator, the human cathelicidin-derived peptide LL37, induces IL-1 beta processing and release. J. Immunol. 172:4987–4994. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

