Combination therapy using the cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor Parecoxib and radioimmunotherapy in nude mice with small peritoneal metastases of colonic origin
- PMID: 15868166
- PMCID: PMC11030210
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-005-0704-3
Combination therapy using the cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor Parecoxib and radioimmunotherapy in nude mice with small peritoneal metastases of colonic origin
Abstract
Background: Inhibition of the COX-2 enzyme has been shown to have a radiosensitizing effect in epithelial cancers. The aim of this study was to investigate whether the efficacy of radioimmunotherapy (RIT) using 131I-labeled anti-CEA monoclonal antibody MN-14 could be enhanced by co-administration of the selective COX-2 inhibitor Parecoxib in mice with small volume (1-3 mm) peritoneal carcinomatosis of colonic origin.
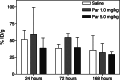
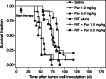
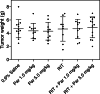
Methods: First, the efficacy of 14 daily injections of Parecoxib monotherapy (0-0.2-1.0-5.0-25.0 mg/kg) was determined in mice with intraperitoneal LS174T xenografts. Second, the influence of Parecoxib (1.0 or 5.0 mg/kg) on the biodistribution of 125I-MN-14 was assessed. Finally, the efficacy of RIT alone [125 microCi 131I-MN-14/mouse approximately 1/4 of the maximal tolerated dose (MTD)] was compared with that of Parecoxib monotherapy and RIT combined with daily injections of Parecoxib (1.0 or 5.0 mg/kg).
Results: Parecoxib had no measurable antitumor effect up to the highest dose level (25 mg/kg). Parecoxib had no effect on the uptake of 125I-MN-14 in the intraperitoneal tumor xenografts or on normal tissue distribution. Median survival of the control mice and the mice treated with Parecoxib monotherapy (1.0 or 5.0 mg/kg) was 48.5 days, 52 days and 52 days (P=0.47). RIT alone significantly delayed the growth of the intraperitoneal xenografts resulting in a median survival of 87 days (P<0.0001). Mice treated with RIT + Parecoxib at 1.0 or 5.0 mg/kg had a median survival of 73.5 days and 76 days, respectively, which was not statistically different from survival after RIT alone (P=0.15).
Conclusion: The COX-2 inhibitor Parecoxib does not enhance the therapeutic efficacy of RIT of experimental small volume peritoneal carcinomatosis of colonic origin.
Figures



References
-
- Koppe MJ, Bleichrodt RP, Oyen WJG, Boerman OC (2005) Radioimmunotherapy of colorectal cancer. Br J Surg (in press) - PubMed
-
- Jain RK. Physiological barriers to delivery of monoclonal antibodies and other macromolecules in tumors. Cancer Res. 1990;50:814s–819s. - PubMed
-
- Juweid M, Sharkey RM, Behr T, Swayne LC, Herskovic T, Pereira M, Rubin AD, Hanley D, Dunn R, Siegel J, Goldenberg DM. Radioimmunotherapy of medullary thyroid cancer with iodine-131-labeled anti-CEA antibodies. J Nucl Med. 1996;37:905–911. - PubMed
-
- Schlom J, Eggensperger D, Colcher D, Molinolo A, Houchens D, Miller LS, Hinkle G, Siler K. Therapeutic advantage of high-affinity anticarcinoma radioimmunoconjugates. Cancer Res. 1992;52:1067–1072. - PubMed
-
- Behr TM, Blumenthal RD, Memtsoudis S, Sharkey RM, Gratz S, Becker W, Goldenberg DM. Cure of metastatic human colonic cancer in mice with radiolabeled monoclonal antibody fragments. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:4900–4907. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

