Use of EPR power saturation to analyze the membrane-docking geometries of peripheral proteins: applications to C2 domains
- PMID: 15869384
- PMCID: PMC3637887
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.34.040204.144534
Use of EPR power saturation to analyze the membrane-docking geometries of peripheral proteins: applications to C2 domains
Abstract
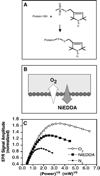
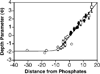
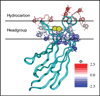
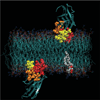
Despite the central importance of peripheral membrane proteins to cellular signaling and metabolic pathways, the structures of protein-membrane interfaces remain largely inaccessible to high-resolution structural methods. In recent years a number of laboratories have contributed to the development of an electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) power saturation approach that utilizes site-directed spin labeling to determine the key geometric parameters of membrane-docked proteins, including their penetration depths and angular orientations relative to the membrane surface. Representative applications to Ca(2+)-activated, membrane-docking C2 domains are described.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of PIP2 binding on the membrane docking geometry of PKC alpha C2 domain: an EPR site-directed spin-labeling and relaxation study.Biochemistry. 2008 Aug 12;47(32):8301-16. doi: 10.1021/bi800711t. Epub 2008 Jul 9. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18610985 Free PMC article.
-
C2 domain of protein kinase C alpha: elucidation of the membrane docking surface by site-directed fluorescence and spin labeling.Biochemistry. 2003 Feb 11;42(5):1254-65. doi: 10.1021/bi026596f. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12564928 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane-docking loops of the cPLA2 C2 domain: detailed structural analysis of the protein-membrane interface via site-directed spin-labeling.Biochemistry. 2003 Nov 18;42(45):13227-40. doi: 10.1021/bi035119+. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 14609334 Free PMC article.
-
High-field EPR on membrane proteins - crossing the gap to NMR.Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2013 Nov;75:1-49. doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2013. PMID: 24160760 Review.
-
Attaching a spin to a protein -- site-directed spin labeling in structural biology.Acta Biochim Pol. 2007;54(2):235-44. Epub 2007 Jun 14. Acta Biochim Pol. 2007. PMID: 17565387 Review.
Cited by
-
The cellular membrane as a mediator for small molecule interaction with membrane proteins.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Oct;1858(10):2290-2304. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2016.04.016. Epub 2016 May 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27163493 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of specific membrane targeting by C2 domains: localized pools of target lipids enhance Ca2+ affinity.Biochemistry. 2007 Apr 10;46(14):4322-36. doi: 10.1021/bi062140c. Epub 2007 Mar 17. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17367165 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of PIP2 binding on the membrane docking geometry of PKC alpha C2 domain: an EPR site-directed spin-labeling and relaxation study.Biochemistry. 2008 Aug 12;47(32):8301-16. doi: 10.1021/bi800711t. Epub 2008 Jul 9. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18610985 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Membrane Binding Mechanics of Synaptotagmin Isoforms Observed in Atomic Detail.Biochemistry. 2017 Jan 10;56(1):281-293. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00468. Epub 2016 Dec 20. Biochemistry. 2017. PMID: 27997124 Free PMC article.
-
Electrostatic interactions and binding orientation of HIV-1 matrix studied by neutron reflectivity.Biophys J. 2010 Oct 20;99(8):2516-24. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.07.062. Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 20959092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altenbach C, Flitsch SL, Khorana HG, Hubbell WL. Structural studies on transmembrane proteins. 2. Spin labeling of bacteriorhodopsin mutants at unique cysteines. Biochemistry. 1989;28:7806–7812. - PubMed
-
- Altenbach C, Oh KJ, Trabanino RJ, Hideg K, Hubbell WL. Estimation of interresidue distances in spin labeled proteins at physiological temperatures: experimental strategies and practical limitations. Biochemistry. 2001;40:15471–15482. - PubMed
-
- Bai J, Tucker WC, Chapman ER. PIP2 increases the speed of response of synaptotagmin and steers its membrane-penetration activity toward the plasma membrane. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004;11:36–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
