Identification and analysis of vnd/NK-2 homeodomain binding sites in genomic DNA
- PMID: 15870192
- PMCID: PMC1129122
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0502261102
Identification and analysis of vnd/NK-2 homeodomain binding sites in genomic DNA
Abstract
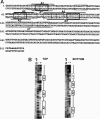
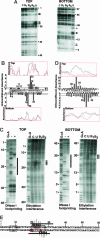
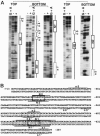
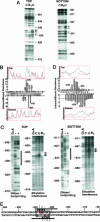
Vnd/NK-2 homeodomain affinity column chromatography was used to purify Drosophila DNA fragments bound by the vnd/NK-2 homeodomain. Sequencing the selected genomic DNA fragments led to the identification of 77 Drosophila DNA fragments that were grouped into 42 vnd/NK-2 homeodomain-binding loci. Most loci were within upstream or intronic regions, especially first introns. Nineteen of the Drosophila DNA fragments cloned correspond to one locus, termed Clone A, which is 312 bp in length and contains five vnd/NK-2 homeodomain core consensus binding sites, 5'-AAGTG, and is part of the first intron of the Beadex gene. We further analyzed the interactions between Clone A and vnd/NK-2 homeodomain protein by mobility-shift assay, DNase I footprinting, methylation interference, and ethylation interference. The DNase I footprinting analysis of Clone A with vnd/NK-2 homeodomain protein revealed three strong binding sites and one weak binding site between 15 and 130 bp of Clone A. We also analyzed binding of the vnd/NK-2 homeodomain to the 5'-flanking sequence of vnd/NK-2 genomic DNA. The DNase I footprinting result showed that there are two strong binding sites and five weak binding sites in the fragment between -385 and -675 bp from the transcription start site of the vnd/NK-2 gene.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Experimental approaches to investigate biophysical interactions between homeodomain transcription factors and DNA.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2025 Mar;1868(1):195074. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2024.195074. Epub 2024 Dec 5. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2025. PMID: 39644990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sequence-specific DNA binding by the vnd/NK-2 homeodomain of Drosophila.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 1;99(20):12721-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.202461199. Epub 2002 Sep 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12232052 Free PMC article.
-
The Nk-2 box of the Drosophila homeodomain protein, Vnd, contributes to its repression activity in a Groucho-dependent manner.Mech Dev. 2007 Jan;124(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2006.07.009. Epub 2006 Aug 2. Mech Dev. 2007. PMID: 17070676
-
Interactions of the vnd/NK-2 homeodomain with DNA by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: basis of binding specificity.Biochemistry. 1997 May 6;36(18):5372-80. doi: 10.1021/bi9620060. Biochemistry. 1997. PMID: 9154919
-
Bugs on drugs go GAGAA.Cell. 2000 Nov 22;103(5):695-8. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00172-0. Cell. 2000. PMID: 11114325 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The HMX/NKX homeodomain protein MLS-2 specifies the identity of the AWC sensory neuron type via regulation of the ceh-36 Otx gene in C. elegans.Development. 2010 Mar;137(6):963-74. doi: 10.1242/dev.044719. Epub 2010 Feb 11. Development. 2010. PMID: 20150279 Free PMC article.
-
The alternative protein isoform NK2B, encoded by the vnd/NK-2 proneural gene, directly activates transcription and is expressed following the start of cells differentiation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jul;39(13):5401-11. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr121. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21422076 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental approaches to investigate biophysical interactions between homeodomain transcription factors and DNA.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2025 Mar;1868(1):195074. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2024.195074. Epub 2024 Dec 5. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2025. PMID: 39644990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of an upstream regulatory element reveals a novel requirement for Ind activity in maintaining ind expression.Mech Dev. 2007 Mar;124(3):230-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2006.11.003. Epub 2006 Dec 3. Mech Dev. 2007. PMID: 17224261 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated cistromic and expression analysis of amplified NKX2-1 in lung adenocarcinoma identifies LMO3 as a functional transcriptional target.Genes Dev. 2013 Jan 15;27(2):197-210. doi: 10.1101/gad.203208.112. Epub 2013 Jan 15. Genes Dev. 2013. PMID: 23322301 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nirenberg, M., Nakayama, K., Nakayama, N., Kim, Y., Mellerick, D., Wang, L.-H., Webber, K. O. & Lad, R. (1995) Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 758, 224-242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

