Potential energy functions for atomic-level simulations of water and organic and biomolecular systems
- PMID: 15870211
- PMCID: PMC1100738
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0408037102
Potential energy functions for atomic-level simulations of water and organic and biomolecular systems
Abstract
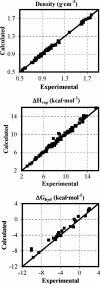
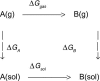
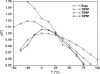
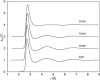
An overview is provided on the development and status of potential energy functions that are used in atomic-level statistical mechanics and molecular dynamics simulations of water and of organic and biomolecular systems. Some topics that are considered are the form of force fields, their parameterization and performance, simulations of organic liquids, computation of free energies of hydration, universal extension for organic molecules, and choice of atomic charges. The discussion of water models covers some history, performance issues, and special topics such as nuclear quantum effects.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of charge models for fixed-charge force fields: small-molecule hydration free energies in explicit solvent.J Phys Chem B. 2007 Mar 8;111(9):2242-54. doi: 10.1021/jp0667442. Epub 2007 Feb 10. J Phys Chem B. 2007. PMID: 17291029
-
MC-PHS: a Monte Carlo implementation of the primary hydration shell for protein folding and design.Biophys J. 2003 Feb;84(2 Pt 1):805-15. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74900-5. Biophys J. 2003. PMID: 12547765 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of the interfacial water content in protein-protein complexes from free energy simulations.Biophys J. 2006 Feb 1;90(3):841-50. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.065524. Epub 2005 Nov 11. Biophys J. 2006. PMID: 16284258 Free PMC article.
-
How well can simulation predict protein folding kinetics and thermodynamics?Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2005;34:43-69. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.34.040204.144447. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2005. PMID: 15869383 Review.
-
Modeling water, the hydrophobic effect, and ion solvation.Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2005;34:173-99. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.34.040204.144517. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2005. PMID: 15869376 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Dynamics Studies of Therapeutic Liquid Mixtures and Their Binding to Mycobacteria.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 20;12:626735. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.626735. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33959006 Free PMC article.
-
Melting Points of OPC and OPC3 Water Models.ACS Omega. 2020 Sep 22;5(39):25087-25094. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c02638. eCollection 2020 Oct 6. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 33043187 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial activity of compounds identified by artificial intelligence discovery engine targeting enzymes involved in Neisseria gonorrhoeae peptidoglycan metabolism.Biol Res. 2024 Sep 5;57(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s40659-024-00543-9. Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 39238057 Free PMC article.
-
FF12MC: A revised AMBER forcefield and new protein simulation protocol.Proteins. 2016 Oct;84(10):1490-516. doi: 10.1002/prot.25094. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Proteins. 2016. PMID: 27348292 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the Ion, Solvent, and Thermal Interaction Coefficients on Battery Voltage.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 Feb 21;146(7):4592-4604. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c11589. Epub 2024 Feb 10. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 38340142 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barker, J. A. & Watts, R. O. (1969) Chem. Phys. Lett. 3, 144–145.
-
- Rahman, A. & Stillinger, F. H. (1971) J. Chem. Phys. 55, 3336–3359.
-
- Stillinger, F. H & Rahman, A. (1974) J. Chem. Phys. 60, 1545–1557.
-
- Tirado-Rives, J. & Jorgensen, W. L. (1990) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 112, 2773–2781.
-
- Guillot, B. (2002) J. Mol. Liquids 101, 219–260.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

