RNA-guided RNA modification: functional organization of the archaeal H/ACA RNP
- PMID: 15870259
- PMCID: PMC1132009
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1309605
RNA-guided RNA modification: functional organization of the archaeal H/ACA RNP
Abstract
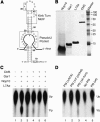
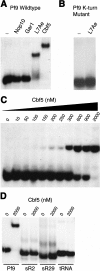
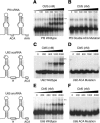
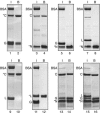
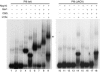
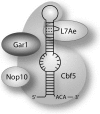
In eukaryotes and archaea, uridines in various RNAs are converted to pseudouridines by RNA-guided RNA modification complexes termed H/ACA RNPs. Guide RNAs within the complexes base-pair with target RNAs to direct modification of specific ribonucleotides. Cbf5, a protein component of the complex, likely catalyzes the modification. However, little is known about the organization of H/ACA RNPs and the roles of the multiple proteins thought to comprise the complexes. We have reconstituted functional archaeal H/ACA RNPs from recombinant components, defined the components necessary and sufficient for function, and determined the direct RNA-protein and protein-protein interactions that occur between the components. The results provide substantial insight into the functional organization of this RNP. The functional complex requires a guide RNA and each of four proteins: Cbf5, Gar1, L7Ae, and Nop10. Two proteins interact directly with the guide RNA: L7Ae and Cbf5. L7Ae does not interact with other H/ACA RNP proteins in the absence of the RNA. We have defined two novel functions for Cbf5. Cbf5 is the protein that specifically recognizes and binds H/ACA guide RNAs. In addition, Cbf5 recruits the two other essential proteins, Gar1 and Nop10, to the pseudouridylation guide complex.
Figures
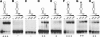
References
-
- Aittaleb M., Rashid, R., Chen, Q., Palmer, J.R., Daniels, C.J., and Li, H. 2003. Structure and function of archaeal box C/D sRNP core proteins. Nat. Struct. Biol. 10: 256–263. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. 2004. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431: 350–355. - PubMed
-
- Aravind L. and Koonin, E.V. 2001. THUMP—A predicted RNA-binding domain shared by 4-thiouridine, pseudouridine synthases and RNA methylases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 26: 215–217. - PubMed
-
- Bachellerie J.-P. and Cavaille, J. 1998. Small nucleolar RNAs guide the ribose methylations of eukaryotic rRNAs. In Modification and editing of RNA (eds. H. Grosjean and B. Benne), pp. 255–272. ASM Press, Washington, DC.
-
- Balakin A.G., Smith, L., and Fournier, M.J. 1996. The RNA world of the nucleolus: Two major families of small RNAs defined by different box elements with related functions. Cell 86: 823–834. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
