MyoD targets chromatin remodeling complexes to the myogenin locus prior to forming a stable DNA-bound complex
- PMID: 15870273
- PMCID: PMC1087700
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.10.3997-4009.2005
MyoD targets chromatin remodeling complexes to the myogenin locus prior to forming a stable DNA-bound complex
Abstract
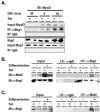
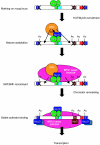
The activation of muscle-specific gene expression requires the coordinated action of muscle regulatory proteins and chromatin-remodeling enzymes. Microarray analysis performed in the presence or absence of a dominant-negative BRG1 ATPase demonstrated that approximately one-third of MyoD-induced genes were highly dependent on SWI/SNF enzymes. To understand the mechanism of activation, we performed chromatin immunoprecipitations analyzing the myogenin promoter. We found that H4 hyperacetylation preceded Brg1 binding in a MyoD-dependent manner but that MyoD binding occurred subsequent to H4 modification and Brg1 interaction. In the absence of functional SWI/SNF enzymes, muscle regulatory proteins did not bind to the myogenin promoter, thereby providing evidence for SWI/SNF-dependent activator binding. We observed that the homeodomain factor Pbx1, which cooperates with MyoD to stimulate myogenin expression, is constitutively bound to the myogenin promoter in a SWI/SNF-independent manner, suggesting a two-step mechanism in which MyoD initially interacts indirectly with the myogenin promoter and attracts chromatin-remodeling enzymes, which then facilitate direct binding by MyoD and other regulatory proteins.
Figures




References
-
- Agalioti, T., S. Lomvardas, B. Parekh, J. Yie, T. Maniatis, and D. Thanos. 2000. Ordered recruitment of chromatin modifying and general transcription factors to the IFN-beta promoter. Cell 103:667-678. - PubMed
-
- Bergstrom, D. A., B. H. Penn, A. Strand, R. L. Perry, M. A. Rudnicki, and S. J. Tapscott. 2002. Promoter-specific regulation of MyoD binding and signal transduction cooperate to pattern gene expression. Mol. Cell 9:587-600. - PubMed
-
- Berkes, C., D. A. Bergstrom, B. H. Penn, K. J. Sever, S. Knoepfler, and S. J. Tapscott. 2004. Pbx and Meis mark genes for activation by MyoD indicating a role for homeodomain genes in establishing myogenic potential. Mol. Cell 14:465-477. - PubMed
-
- Brown, S. A., A. N. Imbalzano, and R. E. Kingston. 1996. Activator-dependent regulation of transcriptional pausing on nucleosomal templates. Genes Dev. 10:1479-1490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
