The LIM protein Ajuba influences interleukin-1-induced NF-kappaB activation by affecting the assembly and activity of the protein kinase Czeta/p62/TRAF6 signaling complex
- PMID: 15870274
- PMCID: PMC1087715
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.10.4010-4022.2005
The LIM protein Ajuba influences interleukin-1-induced NF-kappaB activation by affecting the assembly and activity of the protein kinase Czeta/p62/TRAF6 signaling complex
Abstract
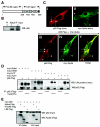
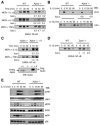
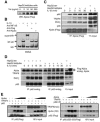
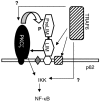
The Zyxin/Ajuba family of cytosolic LIM domain-containing proteins has the potential to shuttle from sites of cell adhesion into the nucleus and thus can be candidate transducers of environmental signals. To understand Ajuba's role in signal transduction pathways, we performed a yeast two-hybrid screen with the LIM domain region of Ajuba. We identified the atypical protein kinase C (aPKC) scaffold protein p62 as an Ajuba binding partner. A prominent function of p62 is the regulation of NF-kappaB activation in response to interleukin-1 (IL-1) and tumor necrosis factor signaling through the formation of an aPKC/p62/TRAF6 multiprotein signaling complex. In addition to p62, we found that Ajuba also interacted with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) and PKCzeta. Ajuba recruits TRAF6 to p62 and in vitro activates PKCzeta activity and is a substrate of PKCzeta. Ajuba null mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and lungs were defective in NF-kappaB activation following IL-1 stimulation, and in lung IKK activity was inhibited. Overexpression of Ajuba in primary MEFs enhances NF-kappaB activity following IL-1 stimulation. We propose that Ajuba is a new cytosolic component of the IL-1 signaling pathway modulating IL-1-induced NF-kappaB activation by influencing the assembly and activity of the aPKC/p62/TRAF6 multiprotein signaling complex.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The interaction of p62 with RIP links the atypical PKCs to NF-kappaB activation.EMBO J. 1999 Jun 1;18(11):3044-53. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.11.3044. EMBO J. 1999. PMID: 10356400 Free PMC article.
-
The atypical PKC-interacting protein p62 channels NF-kappaB activation by the IL-1-TRAF6 pathway.EMBO J. 2000 Apr 3;19(7):1576-86. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.7.1576. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 10747026 Free PMC article.
-
TRIP6 is a RIP2-associated common signaling component of multiple NF-kappaB activation pathways.J Cell Sci. 2005 Feb 1;118(Pt 3):555-63. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01641. Epub 2005 Jan 18. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 15657077
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
Signal integration and diversification through the p62 scaffold protein.Trends Biochem Sci. 2007 Feb;32(2):95-100. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.12.002. Epub 2006 Dec 15. Trends Biochem Sci. 2007. PMID: 17174552 Review.
Cited by
-
AJUBA promotes the migration and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells through upregulation of MMP10 and MMP13 expression.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 14;7(24):36407-36418. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9239. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27172796 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine inhibits inflammatory reaction in lung tissues of septic rats by suppressing TLR4/NF-κB pathway.Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:562154. doi: 10.1155/2013/562154. Epub 2013 Apr 8. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 23690665 Free PMC article.
-
LIM protein Ajuba functions as a nuclear receptor corepressor and negatively regulates retinoic acid signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 16;107(7):2938-43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0908656107. Epub 2010 Jan 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20133701 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of AJUBA, YAP1, and MMP14 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018 Dec 1;11(12):6018-6024. eCollection 2018. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. PMID: 31949690 Free PMC article.
-
YOD1/TRAF6 association balances p62-dependent IL-1 signaling to NF-κB.Elife. 2017 Feb 28;6:e22416. doi: 10.7554/eLife.22416. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28244869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arch, R. H., R. W. Gedrich, and C. B. Thompson. 1998. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs)—a family of adapter proteins that regulates life and death. Genes Dev. 12:2821-2830. - PubMed
-
- Bach, I. 2000. The LIM domain: regulation by association. Mech. Dev. 91:5-17. - PubMed
-
- Burstein, E., and C. S. Duckett. 2003. Dying for NF-κB? Control of cell death by transcriptional regulation of the apoptotic machinery. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15:732-737. - PubMed
-
- Crawford, A. W., and M. C. Beckerle. 1991. Purification and characterization of zyxin, an 82,000-dalton component of adherens junctions. J. Biol. Chem. 266:5847-5853. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
