The S1P2 receptor negatively regulates platelet-derived growth factor-induced motility and proliferation
- PMID: 15870293
- PMCID: PMC1087716
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.10.4237-4249.2005
The S1P2 receptor negatively regulates platelet-derived growth factor-induced motility and proliferation
Abstract
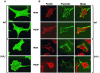
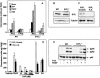
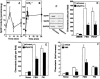
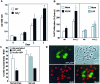
Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), a bioactive sphingolipid metabolite, is the ligand for five specific G protein-coupled receptors, named S1P(1) to S1P(5). In this study, we found that cross-communication between platelet-derived growth factor receptor and S1P(2) serves as a negative damper of PDGF functions. Deletion of the S1P(2) receptor dramatically increased migration of mouse embryonic fibroblasts toward S1P, serum, and PDGF but not fibronectin. This enhanced migration was dependent on expression of S1P(1) and sphingosine kinase 1 (SphK1), the enzyme that produces S1P, as revealed by downregulation of their expression with antisense RNA and small interfering RNA, respectively. Although S1P(2) deletion had no significant effect on tyrosine phosphorylation of the PDGF receptors or activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 or Akt induced by PDGF, it reduced sustained PDGF-dependent p38 phosphorylation and markedly enhanced Rac activation. Surprisingly, S1P(2)-null cells not only exhibited enhanced proliferation but also markedly increased SphK1 expression and activity. Conversely, reintroduction of S1P(2) reduced DNA synthesis and expression of SphK1. Thus, S1P(2) serves as a negative regulator of PDGF-induced migration and proliferation as well as SphK1 expression. Our results suggest that a complex interplay between PDGFR and S1P receptors determines their functions.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate, a platelet-derived lysophospholipid mediator, negatively regulates cellular Rac activity and cell migration in vascular smooth muscle cells.Circ Res. 2002 Feb 22;90(3):325-32. doi: 10.1161/hh0302.104455. Circ Res. 2002. PMID: 11861422
-
The sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor S1P2 triggers hepatic wound healing.FASEB J. 2007 Jul;21(9):2005-13. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-6889com. Epub 2007 Mar 6. FASEB J. 2007. PMID: 17341687
-
G12/13 and Gq mediate S1P2-induced inhibition of Rac and migration in vascular smooth muscle in a manner dependent on Rho but not Rho kinase.Cardiovasc Res. 2008 Sep 1;79(4):689-97. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn118. Epub 2008 May 14. Cardiovasc Res. 2008. PMID: 18480127
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling in physiology and diseases.Biofactors. 2012 Sep-Oct;38(5):329-37. doi: 10.1002/biof.1030. Epub 2012 Jun 7. Biofactors. 2012. PMID: 22674845 Review.
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling: providing cells with a sense of direction.Trends Cell Biol. 2002 May;12(5):236-42. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(02)02277-8. Trends Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12062172 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of ABCC1 in export of sphingosine-1-phosphate from mast cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Oct 31;103(44):16394-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0603734103. Epub 2006 Oct 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17050692 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes PDGF-dependent endothelial progenitor cell angiogenesis in human chondrosarcoma cells.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Dec 6;11(23):11040-11053. doi: 10.18632/aging.102508. Epub 2019 Dec 6. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31809267 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus regulates bioactive sphingolipids.J Biol Chem. 2008 Sep 19;283(38):26148-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M710181200. Epub 2008 Jul 20. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18644793 Free PMC article.
-
Proximal tubule sphingosine kinase-1 has a critical role in A1 adenosine receptor-mediated renal protection from ischemia.Kidney Int. 2012 Oct;82(8):878-91. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.224. Epub 2012 Jun 13. Kidney Int. 2012. PMID: 22695326 Free PMC article.
-
Expansion of Sphingosine Kinase and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor Function in Normal and Cancer Cells: From Membrane Restructuring to Mediation of Estrogen Signaling and Stem Cell Programming.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 31;19(2):420. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020420. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29385066 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allende, M. L., T. Yamashita, and R. L. Proia. 2003. G-protein coupled receptor S1P1 acts within endothelial cells to regulate vascular maturation. Blood 102:3665-3667. - PubMed
-
- Anliker, B., and J. Chun. 2004. Lysophospholipid G protein-coupled receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 279:20555-20558. - PubMed
-
- Baudhuin, L. M., K. L. Cristina, J. Lu, and Y. Xu. 2002. Akt activation induced by lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine-1-phosphate requires both mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and is cell-line specific. Mol. Pharmacol. 62:660-671. - PubMed
-
- Baudhuin, L. M., Y. Jiang, A. Zaslavsky, I. Ishii, J. Chun, and Y. Xu. 2004. S1P3-mediated Akt activation and cross-talk with platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR). FASEB J. 18:341-343. - PubMed
-
- Bokoch, G. M. 2003. Biology of the p21-activated kinases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72:743-781. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
