Co-expression of RON and MET is a prognostic indicator for patients with transitional-cell carcinoma of the bladder
- PMID: 15870710
- PMCID: PMC2361770
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602593
Co-expression of RON and MET is a prognostic indicator for patients with transitional-cell carcinoma of the bladder
Abstract
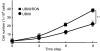
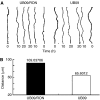
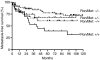
Recepteur d'Origine Nantais (RON) is a distinct receptor tyrosine kinase in the c-met proto-oncogene family. We examined the mutational and expression patterns of RON in eight human uroepithelial cell lines. Biological effects of RON overexpression on cancer cells were investigated in vitro, and the prognostic significance of RON and/or c-met protein (MET) expression was analysed in a bladder cancer cohort (n=183). There was no evidence of mutation in the kinase domain of RON. Overexpression of RON using an inducible Tet-off system induced increased cell proliferation, motility, and antiapoptosis. Immunohistochemical analysis showed that RON was overexpressed in 60 cases (32.8%) of primary tumours, with 14 (23.3%) showing a high level of expression. Recepteur d'Origine Nantais expression was positively associated with histological grading, larger size, nonpapillary contour, and tumour stage (all P<0.01). In addition, MET was overexpressed in 82 cases (44.8%). Co-expressed RON and MET was significantly associated with decreased overall survival (P=0.005) or metastasis-free survival (P=0.01) in 35 cases (19.1%). Recepteur d'Origine Nantais-associated signalling may play an important role in the progression of human bladder cancer. Evaluation of RON and MET expression status may identify a subset of bladder-cancer patients who require more intensive treatment.
Figures




References
-
- Adam RM, Roth JA, Cheng HL, Rice DC, Khoury J, Bauer SB, Peters CA, Freeman MR (2003) Signaling through PI3K/Akt mediates stretch and PDGF-BB-dependent DNA synthesis in bladder smooth muscle cells. J Urol 169: 2388–2393 - PubMed
-
- Angeloni D, Danilkovitch-Miagkova A, Ivanov SV, Breathnach R, Johnson BE, Leonard EJ, Lerman MI (2000) Gene structure of the human receptor tyrosine kinase RON and mutation analysis in lung cancer samples. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 29: 147–156, doi: 10.1002/1098-2264 (2000)9999:9999〈::AID-GCC1015〉3.0.CO;2-N - PubMed
-
- Chen Q, Seol DW, Carr B, Zarnegar R (1997) Co-expression and regulation of Met and Ron proto-oncogenes in human hepatocellular carcinoma tissues and cell lines. Hepatology 26: 59–66, doi: 10.1002/hep.510260108 - PubMed
-
- Chen YQ, Zhou YQ, Fisher JH, Wang MH (2002) Targeted expression of the receptor tyrosine kinase RON in distal lung epithelial cells results in multiple tumor formation: oncogenic potential of RON in vivo. Oncogene 21: 6382–6386, doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205783 - PubMed
-
- Cheng HL, Trink B, Tzai TS, Liu HS, Chan SH, Ho CL, Sidransky D, Chow NH (2002) Overexpression of c-met as a prognostic indicator for transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. A comparison with p53 nuclear accumulation. J Clin Oncol 20: 1544–1550 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

