Biotin-responsive basal ganglia disease maps to 2q36.3 and is due to mutations in SLC19A3
- PMID: 15871139
- PMCID: PMC1226189
- DOI: 10.1086/431216
Biotin-responsive basal ganglia disease maps to 2q36.3 and is due to mutations in SLC19A3
Abstract
Biotin-responsive basal ganglia disease (BBGD) is a recessive disorder with childhood onset that presents as a subacute encephalopathy, with confusion, dysarthria, and dysphagia, and that progresses to severe cogwheel rigidity, dystonia, quadriparesis, and eventual death, if left untreated. BBGD symptoms disappear within a few days with the administration of high doses of biotin (5-10 mg/kg/d). On brain magnetic resonance imaging examination, patients display central bilateral necrosis in the head of the caudate, with complete or partial involvement of the putamen. All patients diagnosed to date are of Saudi, Syrian, or Yemeni ancestry, and all have consanguineous parents. Using linkage analysis in four families, we mapped the genetic defect near marker D2S2158 in 2q36.3 (LOD=5.9; theta=0.0) to a minimum candidate region (approximately 2 Mb) between D2S2354 and D2S1256, on the basis of complete homozygosity. In this segment, each family displayed one of two different missense mutations that altered the coding sequence of SLC19A3, the gene for a transporter related to the reduced-folate (encoded by SLC19A1) and thiamin (encoded by SLC19A2) transporters.
Figures

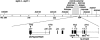
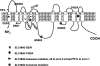

References
Web Resources
-
- BLAST, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/ (for BLASTX, TBLASTN, and BLASTP)
-
- dbSNP, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/SNP/ (for nine novel SNPs in the 5′ UTR, alt3, alt6′, and alt7′ of SLC19A3 and DKFZp547H025 [accession numbers 32476166–32476174])
-
- Fondation Jean Dausset CEPH Web Server, http://www.cephb.fr/ (for CEPH family genotypes used in map construction)
-
- HMMTOP 2.0, http://www.enzim.hu/hmmtop/index.html
-
- Human Genome Database, http://www.gdb.org
References
-
- Aoki Y, Suzuki Y, Sakamoto O, Li X, Takahashi K, Ohtake A, Sakuta R, Ohura T, Miyabayashi S, Narisawa K (1995) Molecular analysis of holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency: a missense mutation and a single base deletion are predominant in Japanese patients. Biochim Biophys Acta 1272:168–174 - PubMed
-
- Balamurugan K, Said HM (2002) Functional role of specific amino acid residues in human thiamine transporter SLC19A2: mutational analysis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 283:G37–G43 - PubMed
-
- Basel-Vanagaite L, Straussberg R, Ovadia H, Kaplan A, Magal N, Shorer Z, Shalev H, Walsh C, Shohat M (2004) Infantile bilateral striatal necrosis maps to chromosome 19q. Neurology 62:87–90 - PubMed
-
- Buck SH, Burks TF, Brown MR, Yamamura HI (1981) Reduction in basal ganglia and substantia nigra substance P levels in Huntington’s disease. Brain Res 209:464–469 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

