Comparative molecular analysis of Haemophilus influenzae isolates from young children with acute lower respiratory tract infections and meningitis in Hanoi, Vietnam
- PMID: 15872287
- PMCID: PMC1153806
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.43.5.2474-2476.2005
Comparative molecular analysis of Haemophilus influenzae isolates from young children with acute lower respiratory tract infections and meningitis in Hanoi, Vietnam
Abstract
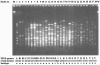
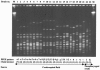
Thirty-seven Haemophilus influenzae strains from nasopharyngeal swabs (NP) and 44 H. influenzae strains from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) were investigated. Of the 37 H. influenzae isolates from NP, the serotypes of 30 isolates were nontypeable, 4 were type b, 2 were type c, and 1 was type a, whereas all of the 44 isolates from CSF were type b. The MICs of 16 antibiotics for the H. influenzae isolates from NP and CSF were similar, and no beta-lactamase-negative ampicillin-resistant strain was found. Molecular typing by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) showed that the 37 H. influenzae strains from NP had 22 PFGE patterns, with none predominating, and the 44 H. influenzae strains from CSF had 9 PFGE patterns, with patterns alpha (22 isolates) and beta (12 isolates) predominating. Our results indicate that two predominant types of H. influenzae type b strains have the potential to spread among children with meningitis in Hanoi, Vietnam.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Low rate of nasopharyngeal carriage and high rate of ampicillin resistance for Haemophilus influenzae among healthy children younger than 5 years old in northern Taiwan.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2008 Feb;41(1):32-40. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2008. PMID: 18327424
-
Molecular typing of Haemophilus influenzae using a DNA probe and multiplex PCR.Mol Cell Probes. 1994 Feb;8(1):23-37. doi: 10.1006/mcpr.1994.1004. Mol Cell Probes. 1994. PMID: 8028605
-
Mutant ftsI genes in the emergence of penicillin-binding protein-mediated beta-lactam resistance in Haemophilus influenzae in Norway.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010 Aug;16(8):1117-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.03052.x. Epub 2009 Sep 8. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010. PMID: 19737286
-
[Clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment of Haemophilus influenzae infection].An Med Interna. 2000 Apr;17(4):204-12. An Med Interna. 2000. PMID: 10893774 Review. Spanish.
-
Recurrent posttraumatic meningitis due to nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: case report and review of the literature.Infection. 2008 Feb;36(1):74-7. doi: 10.1007/s15010-007-6048-5. Epub 2007 Oct 9. Infection. 2008. PMID: 17926006 Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid assessment of Hib disease burden in Vietnam.BMC Public Health. 2011 Apr 25;11:260. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-11-260. BMC Public Health. 2011. PMID: 21513577 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barbour, M. L., R. T. Mayon-White, C. Coles, D. W. Crook, and E. R. Moxon. 1995. The impact of conjugate vaccine on carriage of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J. Infect. Dis. 171:93-98. - PubMed
-
- Faden, H., L. Duffy, R. Wasielewski, J. Wolf, D. Krystofik, and Y. Tung. 1997. Relationship between nasopharyngeal colonization and the development of otitis media in children. J. Infect. Dis. 175:1440-1445. - PubMed
-
- Hoban, D., and D. Felmingham. 2002. The PROTEKT surveillance study: antimicrobial susceptibility of Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis from community-acquired respiratory tract infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 50:49-59. - PubMed
-
- Karlowsky, J. A., I. A. Critchley, R. S. Blosser-Middleton, E. A. Karginova, M. E. Jones, C. Thornsberry, and D. F. Sahm. 2002. Antimicrobial surveillance of Haemophilus influenzae in the United States during 2000-2001 leads to detection of clonal dissemination of a beta-lactamase-negative and ampicillin-resistant strain. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40:1063-1066. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

