Structural requirements for in vivo detection of cell death with 99mTc-annexin V
- PMID: 15872355
- PMCID: PMC1201384
Structural requirements for in vivo detection of cell death with 99mTc-annexin V
Abstract
(99m)Tc-Annexin V is used to image cell death in vivo via high-affinity binding to exposed phosphatidylserine. We investigated how changes in membrane-binding affinity, molecular charge, and method of labeling affected its biodistribution in normal mice and its uptake in apoptotic tissues.
Methods: An endogenous Tc chelation site (Ala-Gly-Gly-Cys-Gly-His) was added to the N-terminus of annexin V to create annexin V-128. The membrane-binding affinity of annexin V-128 was then progressively reduced by 1-4 mutations in calcium-binding sites. In addition, mutations were made in other residues that altered molecular charge without altering membrane-binding affinity. All mutant proteins were labeled with (99m)Tc at the same N-terminal endogenous chelation site. Wild-type annexin V was also labeled with (99m)Tc after derivatization with hydrazinonicotinamide (HYNIC). Radiolabeled proteins were tested for biodistribution in normal mice and in mice treated to induce apoptosis of the liver.
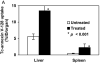
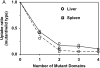
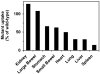
Results: Comparison of (99m)Tc-annexin V-128 with (99m)Tc-HYNIC-annexin V showed that the protein labeled at the endogenous chelation site had the same or higher uptake in apoptotic tissues, while showing 88% lower renal uptake at 60 min after injection. The blood clearance of annexin V was unaffected by changes in either the membrane-binding affinity or the molecular charge. Kidney uptake was unaffected by changes in binding affinity. In marked contrast, uptake in normal liver and spleen decreased markedly as affinity decreased. The same pattern was observed in animals treated with cycloheximide to induce apoptosis. Control experiments with charge mutants showed that the effects seen with the affinity mutants were not due to the concomitant change in molecular charge that occurs in these mutants.
Conclusion: (a) All four domains of annexin V are required for optimal uptake in apoptotic tissues; molecules with only 1 or 2 active domains are unlikely to be suitable for imaging of cell death in vivo. (b) Uptake in normal liver and spleen is specific (dependent on phosphatidylserine-binding affinity), whereas renal uptake is nonspecific. (c) (99m)Tc-Annexin V-128 detects cell death as well as (99m)Tc-HYNIC-annexin V, while showing 88% less renal retention of radioactivity due to much more rapid urinary excretion of radioactivity.
Figures






References
-
- Blankenberg FG, Katsikis PD, Tait JF, et al. Imaging of apoptosis (programmed cell death) with 99mTc annexin V. J Nucl Med. 1999;40:184–191. - PubMed
-
- Thiagarajan P, Tait JF. Binding of annexin V/placental anticoagulant protein I to platelets. Evidence for phosphatidylserine exposure in the procoagulant response of activated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:17420–17423. - PubMed
-
- Fadok VA, Voelker DR, Campbell PA, Cohen JJ, Bratton DL, Henson PM. Exposure of phosphatidylserine on the surface of apoptotic lymphocytes triggers specific recognition and removal by macrophages. J Immunol. 1992;148:2207–2216. - PubMed
-
- Huber R, Berendes R, Burger A, et al. Crystal and molecular structure of human annexin V after refinement. Implications for structure, membrane binding and ion channel formation of the annexin family of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1992;223:683–704. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
