Systematic interpretation of genetic interactions using protein networks
- PMID: 15877074
- PMCID: PMC2814446
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt1096
Systematic interpretation of genetic interactions using protein networks
Abstract
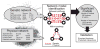
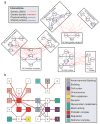
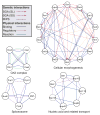
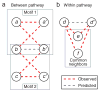
Genetic interaction analysis,in which two mutations have a combined effect not exhibited by either mutation alone, is a powerful and widespread tool for establishing functional linkages between genes. In the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, ongoing screens have generated >4,800 such genetic interaction data. We demonstrate that by combining these data with information on protein-protein, prote in-DNA or metabolic networks, it is possible to uncover physical mechanisms behind many of the observed genetic effects. Using a probabilistic model, we found that 1,922 genetic interactions are significantly associated with either between- or within-pathway explanations encoded in the physical networks, covering approximately 40% of known genetic interactions. These models predict new functions for 343 proteins and suggest that between-pathway explanations are better than within-pathway explanations at interpreting genetic interactions identified in systematic screens. This study provides a road map for how genetic and physical interactions can be integrated to reveal pathway organization and function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Guarente L. Synthetic enhancement in gene interaction: a genetic tool come of age. Trends Genet. 1993;9:362–366. - PubMed
-
- Thomas JH. Thinking about genetic redundancy. Trends Genet. 1993;9:395–399. - PubMed
-
- Hartman JL, Garvik B, Hartwell L. Principles for the buffering of genetic variation. Science. 2001;291:1001–1004. - PubMed
-
- Sham P. Shifting paradigms in gene-mapping methodology for complex traits. Pharmacogenomics. 2001;2:195–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

