Replication of autism linkage: fine-mapping peak at 17q21
- PMID: 15877280
- PMCID: PMC1196442
- DOI: 10.1086/430278
Replication of autism linkage: fine-mapping peak at 17q21
Abstract
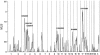
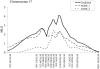
Autism is a heritable but genetically complex disorder characterized by deficits in language and in reciprocal social interactions, combined with repetitive and stereotypic behaviors. As with many genetically complex disorders, numerous genome scans reveal inconsistent results. A genome scan of 345 families from the Autism Genetic Resource Exchange (AGRE) (AGRE_1), gave the strongest evidence of linkage at 17q11-17q21 in families with no affected females. Here, we report a full-genome scan of an independent sample of 91 AGRE families with 109 affected sibling pairs (AGRE_2) that also shows the strongest evidence of linkage to 17q11-17q21 in families with no affected females. Taken together, these samples provide a replication of linkage to this chromosome region that is, to our knowledge, the first such replication in autism. Fine mapping at 2-centimorgan (cM) intervals in the combined sample of families with no affected females reveals a linkage peak at 66.85 cM, which places this locus at 17q21.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- AGRE, http://www.agre.org
-
- Center for Inherited Disease Research, http://www.cidr.jhmi.edu/
-
- Center for Medical Genetics, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/ (for the Marshfield marker maps)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for autism, Rett syndrome, and fragile-X syndrome)
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2000) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th ed. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
-
- Bailey A, Le Couteur A, Gottesman I, Bolton P, Simonoff E, Yuzda E, Rutter M (1995) Autism as a strongly genetic disorder: evidence from a British twin study. Psychol Med 25:63–77 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

