Autoantibody profiling as early diagnostic and prognostic tool for rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 15878904
- PMCID: PMC1755298
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2005.035691
Autoantibody profiling as early diagnostic and prognostic tool for rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Early treatment prevents progression of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), but diagnosis in early disease is impeded by lack of appropriate diagnostic criteria.
Objective: To study the value of rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide autoantibodies (anti-CCP), and anti-RA33 autoantibodies for diagnosis of RA and prediction of outcome in patients with very early arthritis.
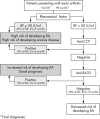
Methods: The prospective follow up inception cohort included 200 patients with very early (<3 months) inflammatory joint disease. Autoantibodies were measured at baseline and analysed in a tree based model which aimed at determining the added diagnostic value of testing for anti-CCP and anti-RA33 as compared with RF alone.
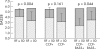
Results: RA was diagnosed in 102 patients, while 98 developed other inflammatory arthropathies. Receiver operator curve analysis showed an optimum cut off level for RF at 50 U/ml, above which anti-CCP and anti-RA33 had no additional diagnostic value. Remarkably, RF >or=50 U/ml and anti-CCP showed similar sensitivity and high specificity for RA, but overlapped considerably. Anti-RA33 was less specific and did not correlate with RF or anti-CCP. Among patients with RA, 72% showed at least one of these three autoantibodies, compared with 15% of non-RA patients. RF >or=50 U/ml and anti-CCP were predictors of erosive disease, whereas anti-RA33 was associated with mild disease.
Conclusions: Stepwise autoantibody testing in early inflammatory joint disease, starting with RF, followed by anti-CCP (in patients with RF <50 U/ml), and finally anti-RA33, should be used as a sensitive and effective strategy for distinguishing patients with RA at high risk for poor outcome.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

