In vitro selection to identify determinants in tRNA for Bacillus subtilis tyrS T box antiterminator mRNA binding
- PMID: 15879350
- PMCID: PMC1090546
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki546
In vitro selection to identify determinants in tRNA for Bacillus subtilis tyrS T box antiterminator mRNA binding
Abstract
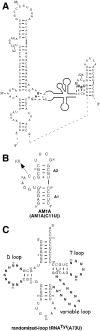
The T box transcription antitermination regulatory system, found in Gram-positive bacteria, is dependent on a complex set of interactions between uncharged tRNA and the 5'-untranslated mRNA leader region of the regulated gene. One of these interactions involves the base pairing of the acceptor end of cognate tRNA with four bases in a 7 nt bulge of the antiterminator RNA. In vitro selection of randomized tRNA binding to Bacillus subtilis tyrS antiterminator model RNAs was used to determine what, if any, sequence trends there are for binding beyond the known base pair complementarity. The model antiterminator RNAs were selected for the wild-type tertiary fold of tRNA. While there were no obvious sequence correlations between the selected tRNAs, there were correlations between certain tertiary structural elements and binding efficiency to different antiterminator model RNAs. In addition, one antiterminator model selected primarily for a kissing tRNA T loop-antiterminator bulge interaction, while another antiterminator model resulted in no such selection. The selection results indicate that, at the level of tertiary structure, there are ideal matches between tRNAs and antiterminator model RNAs consistent with in vivo observations and that additional recognition features, beyond base pair complementarity, may play a role in the formation of the complex.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In vitro structure-function studies of the Bacillus subtilis tyrS mRNA antiterminator: evidence for factor-independent tRNA acceptor stem binding specificity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Feb 15;30(4):1065-72. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.4.1065. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 11842119 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between the acceptor end of tRNA and the T box stimulates antitermination in the Bacillus subtilis tyrS gene: a new role for the discriminator base.J Bacteriol. 1994 Aug;176(15):4518-26. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.15.4518-4526.1994. J Bacteriol. 1994. PMID: 8045882 Free PMC article.
-
Structural transitions induced by the interaction between tRNA(Gly) and the Bacillus subtilis glyQS T box leader RNA.J Mol Biol. 2005 Jun 3;349(2):273-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.03.061. Epub 2005 Apr 8. J Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15890195
-
An evolving tale of two interacting RNAs-themes and variations of the T-box riboswitch mechanism.IUBMB Life. 2019 Aug;71(8):1167-1180. doi: 10.1002/iub.2098. Epub 2019 Jun 17. IUBMB Life. 2019. PMID: 31206978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
tRNA-directed transcription antitermination.Mol Microbiol. 1994 Aug;13(3):381-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00432.x. Mol Microbiol. 1994. PMID: 7527891 Review.
Cited by
-
Interfacing medicinal chemistry with structural bioinformatics: implications for T box riboswitch RNA drug discovery.BMC Bioinformatics. 2012 Mar 13;13 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S5. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-S2-S5. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22536868 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemistry of Aminoacyl tRNA Synthetase and tRNAs and Their Engineering for Cell-Free and Synthetic Cell Applications.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Jul 1;10:918659. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.918659. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35845409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors that influence T box riboswitch efficacy and tRNA affinity.Bioorg Med Chem. 2015 Sep 1;23(17):5702-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2015.07.018. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Bioorg Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26220520 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of neomycin B-binding site in T box antiterminator model RNA.Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Apr 15;16(8):4466-70. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.02.056. Epub 2008 Mar 7. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18329274 Free PMC article.
-
T box transcription antitermination riboswitch: influence of nucleotide sequence and orientation on tRNA binding by the antiterminator element.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Mar;1789(3):185-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.12.004. Epub 2008 Dec 25. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19152843 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grundy F.J., Henkin T.M. tRNA as a positive regulator of transcription antitermination in B.subtilis. Cell. 1993;74:475–482. - PubMed
-
- Rollins S.M., Grundy F.J., Henkin T.M. Analysis of cis-acting sequence and structural elements required for antitermination of the Bacillus subtilis tyrS gene. Mol. Microbiol. 1997;25:411–421. - PubMed
-
- Grundy F.J., Henkin T.M. The T box and S box transcription termination control systems. Front. Biosci. 2003;8:d20–d31. - PubMed
-
- Yousef M.R., Grundy F.J., Henkin T.M. Structural transitions induced by the interaction between tRNAGly and the Bacillus subtilis glyQS T box leader RNA. J. Mol. Biol. 2005 In press. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

