The glucocorticoid receptor blocks P-TEFb recruitment by NFkappaB to effect promoter-specific transcriptional repression
- PMID: 15879558
- PMCID: PMC1091745
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1297105
The glucocorticoid receptor blocks P-TEFb recruitment by NFkappaB to effect promoter-specific transcriptional repression
Abstract
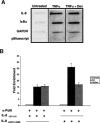
To investigate the determinants of promoter-specific gene regulation by the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), we compared the composition and function of regulatory complexes at two NFkappaB-responsive genes that are differentially regulated by GR. Transcription of the IL-8 and IkappaBalpha genes is stimulated by TNFalpha in A549 cells, but GR selectively represses IL-8 mRNA synthesis by inhibiting Ser2 phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II (pol II) C-terminal domain (CTD). The proximal kappaB elements at these genes differ in sequence by a single base pair, and both recruited RelA and p50. Surprisingly, GR was recruited to both of these elements, despite the fact that GR failed to repress the IkappaBalpha promoter. Rather, the regulatory complexes formed at IL-8 and IkappaBalpha were distinguished by differential recruitment of the Ser2 CTD kinase, P-TEFb. Disruption of P-TEFb function by the Cdk-inhibitor, DRB, or by small interfering RNA selectively blocked TNFalpha stimulation of IL-8 mRNA production. GR competed with P-TEFb recruitment to the IL-8 promoter. Strikingly, IL-8 mRNA synthesis was repressed by GR at a post-initiation step, demonstrating that promoter proximal regulatory sequences assemble complexes that impact early and late stages of mRNA synthesis. Thus, GR accomplishes selective repression by targeting promoter-specific components of NFkappaB regulatory complexes.
Figures
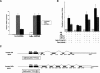

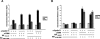
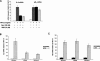

Similar articles
-
Positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) contributes to dengue virus-stimulated induction of interleukin-8 (IL-8).Cell Microbiol. 2010 Nov;12(11):1589-603. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2010.01493.x. Cell Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20618343
-
The glucocorticoid receptor inhibits NFkappaB by interfering with serine-2 phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain.Genes Dev. 2000 Sep 15;14(18):2314-29. doi: 10.1101/gad.827900. Genes Dev. 2000. PMID: 10995388 Free PMC article.
-
Gene-specific requirement for P-TEFb activity and RNA polymerase II phosphorylation within the p53 transcriptional program.Genes Dev. 2006 Mar 1;20(5):601-12. doi: 10.1101/gad.1398206. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16510875 Free PMC article.
-
How glucocorticoid receptors modulate the activity of other transcription factors: a scope beyond tethering.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013 Nov 5;380(1-2):41-54. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2012.12.014. Epub 2012 Dec 23. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23267834 Review.
-
Expanding role of cyclin dependent kinases in cytokine inducible gene expression.Cell Cycle. 2008 Sep 1;7(17):2661-6. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.17.6594. Epub 2008 Sep 12. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18728388 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glucocorticoid repression of inflammatory gene expression shows differential responsiveness by transactivation- and transrepression-dependent mechanisms.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53936. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053936. Epub 2013 Jan 14. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23349769 Free PMC article.
-
Altered subcellular distribution of MSK1 induced by glucocorticoids contributes to NF-kappaB inhibition.EMBO J. 2008 Jun 18;27(12):1682-93. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.95. Epub 2008 May 29. EMBO J. 2008. PMID: 18511904 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid-induced tethered transrepression requires SUMOylation of GR and formation of a SUMO-SMRT/NCoR1-HDAC3 repressing complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Feb 2;113(5):E635-43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1522826113. Epub 2015 Dec 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26712006 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid receptors: finding the middle ground.J Clin Invest. 2017 Apr 3;127(4):1136-1145. doi: 10.1172/JCI88886. Epub 2017 Mar 20. J Clin Invest. 2017. PMID: 28319043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into negative regulation by the glucocorticoid receptor from genome-wide profiling of inflammatory cistromes.Mol Cell. 2013 Jan 10;49(1):158-71. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.10.013. Epub 2012 Nov 15. Mol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23159735 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn S.H., Kim, M., and Buratowski, S. 2004. Phosphorylation of serine 2 within the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain couples transcription and 3′ end processing. Mol. Cell 13: 67–76. - PubMed
-
- Andrulis E.D., Werner, J., Nazarian, A., Erdjument-Bromage, H., Tempst, P., and Lis, J.T. 2002. The RNA processing exosome is linked to elongating RNA polymerase II in Drosophila. Nature 420: 837–841. - PubMed
-
- Barboric M., Nissen, R.M., Kanazawa, S., Jabrane-Ferrat, N., and Peterlin, B.M. 2001. NF-κB binds P-TEFb to stimulate transcriptional elongation by RNA polymerase II. Mol. Cell 8: 327–337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
